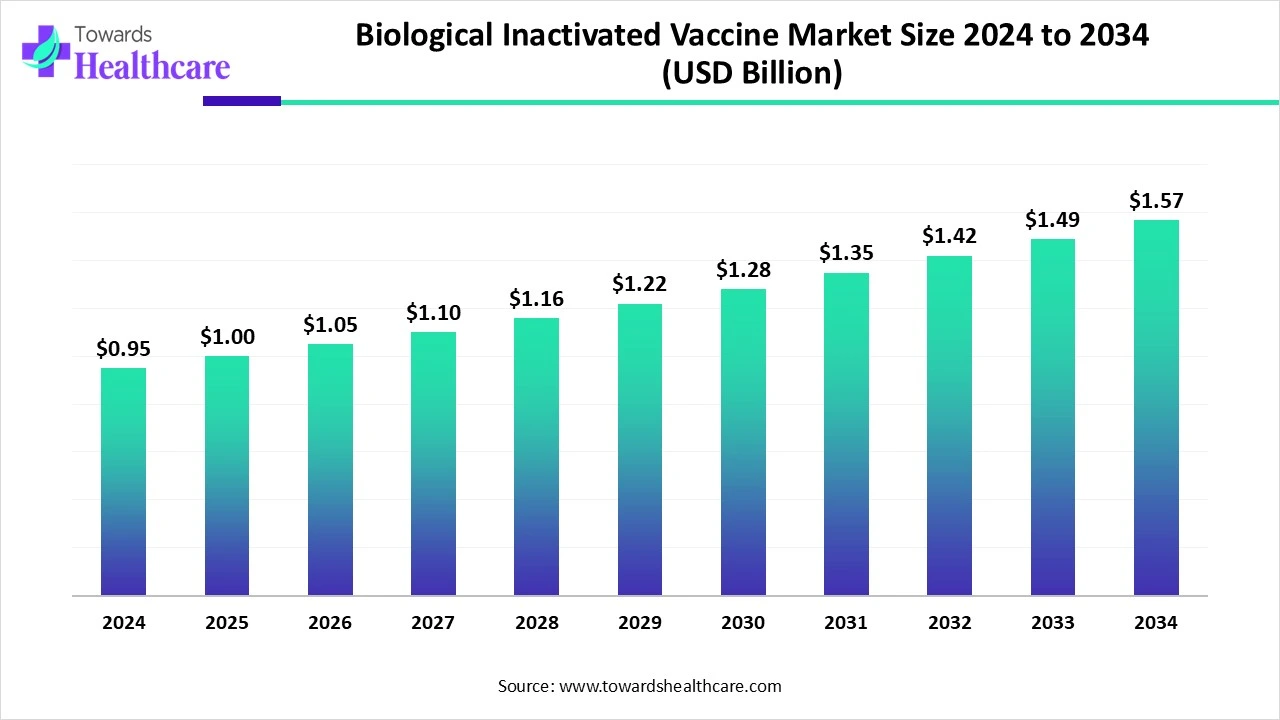
The global biological inactivated vaccine market was USD 0.95B (2024) — rising to USD 1.00B (2025) and projected to reach USD 1.57B by 2034 (a 57% absolute rise / CAGR 5.14% for 2025–2034).
Download the free sample and get the complete insights and forecasts report on this market @ https://www.towardshealthcare.com/download-sample/5932
Market size
Base numbers (anchor data you gave)
●Market size: USD 0.95 billion (2024) → USD 1.00 billion (2025) → USD 1.57 billion (2034 projected). Absolute +USD 0.57B (≈+57%) across 2025–2034; CAGR ≈ 5.14% (2025→2034).
●These figures are the primary quantitative anchors used across this analysis (you provided them).
Year-to-year growth profile (interpretation)
●The market grows steadily (mid-single digits CAGR), which implies a combination of recurring seasonal/annual demand (influenza & routine immunizations) plus episodic demand (outbreaks, campaigns).
●Expect relatively low volatility compared with platform-shift markets (e.g., mRNA) because inactivated vaccines are mature products with steady procurement pipelines.
Value drivers behind the USD figures
●Ongoing seasonal vaccine demand (influenza), large immunization campaigns (polio, rabies in high-risk zones), government procurement, and replacement/booster programs underpin recurring revenues.
●Growing manufacturing investments (esp. in Asia) and improved distribution channels (hospital pharmacies → online pharmacies) lift ASPs and accessible volumes.
Market structure implications
●The market is concentrated by technology (egg-based still dominant ~55–60% in 2024) with pockets of rapid growth (cell culture). That structure limits upside CAGR unless cell-culture scaling accelerates or new inactivated launches expand indications.
Price vs. volume dynamics
●Modest price inflation combined with volume growth (expanded immunization programs in emerging markets) explains the projected USD increase rather than breakthrough pricing events. Procurement tends to be volume-focused (public tenders), constraining price spikes.
Manufacturing footprint and capacity
●Egg-based capacity (legacy influenza lines) represents a sunk asset base; incremental capacity additions are more likely to be cell culture / single-use or regional fill-finish hubs (India/China expansions). India’s share as a supplier (noted in your data) is a structural size multiplier.
Short/medium term market ceilings
●With 57% projected growth to 2034, the ceiling is realistic for a mature category — market expansion hinges on (a) broader adoption in low-income regions, (b) new inactivated launches (e.g., improved influenza formulations, next-gen IPV) and (c) shifts in route-of-administration (intradermal/patch) improving dose efficiency.
Investment implication
●Investors should view this as a steady, lower-risk biotech subsegment with predictable cashflows (government demand), but limited rapid re-rating unless a high-value, large-volume new inactivated product or major technology shift occurs.
Market trends
Asia-Pacific leadership & fastest growth (30–35% revenue share in 2024)
●APAC’s dense population, large public programs and local manufacturers make it the largest & fastest expanding regional market.
Dominance of viral inactivated vaccines (largest vaccine-type share in 2024)
●Viral inactivated vaccines are the biggest segment (influenza is the largest sub-segment with roughly 40–45% share) — seasonal demand and established immunization schedules drive steady volume.
Egg-based manufacturing still dominant (≈55–60% in 2024)
●Legacy influenza manufacturing lines and cost-advantages sustain egg-based shares, even as cell culture methods scale.
Shift to cell culture and alternative processes
●Cell culture-based inactivated vaccines are the fastest-growing production technology (higher scalability, lower animal-product dependence).
Route-of-administration evolution
●Intramuscular delivery dominated in 2024 (60–65%); intradermal routes and patch/inhaled approaches are developing — these can increase dose-efficiency and acceptance.
Distribution channel transition
●Hospital pharmacies held 45–50% share in 2024; online pharmacies expected to grow fastest — e-commerce + telehealth accelerate patient access.
End-user & research activity
●Hospitals dominate end-users (50–55% in 2024). Research institutes are the fastest growth end-user segment, reflecting R&D into new inactivated formulations and production tech.
Public sector procurement & immunization agendas
●Large public immunization programs (national schedules, WHO/UNICEF procurement) continue to be the largest demand engine — immunization agendas (IA2030) reinforce predictable demand cycles.
Product launches & strategic agreements
●Recent tech transfers and new product approvals (e.g., domestic hexavalent transfers, new quadrivalent inactivated influenza vaccines) show manufacturers refreshing portfolios to reduce mismatches & expand market share.
Regulatory & prequalification momentum
●WHO prequalification and national approvals (e.g., Biological E. OPV pre-qualification noted in your content) accelerate global procurement eligibility and export opportunities.
AI impacts / roles
Antigen selection & epitope prediction for inactivated formulations
●AI models (deep learning on viral protein structures and sequence variation) can prioritize strain variants most likely to induce cross-protective antibody responses while preserving epitopes after inactivation. For influenza or pan-H-type programs this reduces strain-mismatch risk and improves seasonal formulation accuracy.
Predictive inactivation-preservation modelling
●Inactivation (formaldehyde, β-propiolactone, heat) can alter antigenic surface. Machine-learned models trained on physicochemical data and immunoassays predict which inactivation parameters preserve neutralizing epitopes, enabling fewer wet-lab iterations and higher retained potency per batch.
Adjuvant-antigen pairing and optimization
●AI screens large datasets (immunogenicity readouts, cytokine profiles, formulation stability) to recommend adjuvant types and concentrations tailored for inactivated antigens, improving immune responses and potentially reducing required antigen dose.
Egg-yield and cell-culture yield forecasting
●For egg-based influenza and cell culture lines, ML models forecast yield variability (per flock/bioreactor batch) using upstream signals (cell health metrics, media sensors, environmental data) to maximize output and reduce failed batches.
Process optimization / digital twins of manufacturing lines
●Create digital twins of inactivation + downstream fill-finish lines. Simulate scale-up scenarios, tweak residence times, temperatures and mixing, and predict CQAs (critical quality attributes) to minimize scale-up surprises and improve GMP reproducibility.
Automated QC & potency analytics (computer vision + ML)
●Automate inspection at fill-finish and integrate ML models to detect particulates, vial defects, or unexpected color changes. Combine with ML potency prediction from surrogate assays to speed batch release.
Adaptive clinical trial design & patient stratification
●ML identifies subpopulations (age, prior immunity) most likely to show robust responses to inactivated formulations. Adaptive trial designs shorten cycle times and reduce sample sizes for bridging studies (e.g., new strain influenza vaccines).
Cold-chain & demand forecasting for distribution optimization
●Combine demand forecasting (seasonality, epidemiology, procurement schedules) with IoT cold-chain sensor data and predictive analytics to optimize allocation; reduces wastage (sensitive for egg-based seasonal vaccines).
Safety surveillance & rapid signal detection (pharmacovigilance)
●Natural language processing and ML analyze global AE reports, social media, EHR signals to detect early safety signals specific to inactivated platforms (e.g., injection-site patterns) enabling faster risk management and targeted communication.
Regulatory dossier automation & knowledge-based submission tooling
●NLP tools extract structured evidence from internal studies and public literature to auto-populate regulatory templates (CMC, stability). For inactivated vaccines, this accelerates lot-release documentation and WHO prequalification support.
Implementation note (how this translates to ROI):
●AI reduces bench cycles (faster antigen/inactivation optimization), cuts failed batches (yield/predictive QC), shortens clinical timelines (adaptive trials), and reduces logistic waste — together these can materially increase effective producible doses and margin for inactivated vaccine manufacturers.
Regional insights
Asia-Pacific (dominant region; 30–35% share in 2024)
Manufacturing scale & export hub
●India: described as 60% of global vaccine production (your content) — large volume capacity, low-cost manufacturing and global supply agreements enable large fill-finish throughput for inactivated vaccines.
●China: high domestic adoption of inactivated COVID-19 vaccines; growing export volumes (you noted ~$1.03B exports for vaccines/biologicals in 2024).
Demand drivers
●High population, public immunization programs, seasonal influenza pockets, and polio eradication campaigns. Procurement via national immunization budgets drives bulk purchases.
Innovation cluster
●Increasing cell-culture facilities, domestic R&D (computational vaccine design), and partnerships (tech transfer, local production of hexavalent formulations).
Regulatory & procurement nuance
●Varied regulatory maturity: some APAC regulators now permit rapid tech transfer and local licensure (e.g., India), which shortens time-to-market for regionally produced inactivated vaccines.
North America
R&D & clinical trial sophistication
●Heavy investment in advanced QC, PAT (process analytical tech), and cell-culture adoption; high share of clinical trials for inactivated formulations in the U.S. (your content: many clinical trials registered).
Premium pricing & private market
●Higher ASPs for specialized vaccines; private payers drive premiums for advanced formulations (adjuvanted, high-dose flu).
Regulatory rigor & quality expectations
●FDA pathways require robust CMC; companies investing here gain reputation and access to global tenders.
Europe
Specialty vaccine firms & technology pilots
●Strong presence of specialized vaccine companies (e.g., Valneva) and pilot manufacturing for new inactivated processes.
Regulatory harmonization
●EMA pathways and EU procurement programs create stable demand; EU funding for domestic manufacturing capacity.
Latin America & Africa
Programmatic demand, donor reliance
●Vaccination largely programmatic (PAHO/UNICEF/WHO backed) — large but price-sensitive tenders; inactivated vaccines used heavily for polio, rabies, JE.
Cold chain / distribution challenges
●Infrastructure limits that increase wastage; online pharmacy growth is slower but rising in urban pockets.
Middle East & Gulf
Investment for capacity & regional hubs
●Sovereign wealth and targeted investment in biotech create opportunities for regional fill-finish hubs serving MEA.
●Cross-regional subpoint — route & distribution: Intramuscular delivery remains the default worldwide; however intradermal and needle-free delivery pilots gain traction in places with dose-sparing needs (important for supply-constrained programs).
Market dynamics
Drivers
●Government immunization programs & IA2030 alignment — large predictable procurement (WHO/UNICEF tenders, national schedules).
●Seasonal & recurrent disease burden (influenza dominance) — consistent annual demand for influenza drives base volumes.
●Manufacturing scale in Asia (India/China) — enables low-cost production, export opportunities and competitive tender wins.
●Technology transfers & partnerships — domestic tech transfer agreements (e.g., Sanofi/Institute example you provided) increase local supply and fill-finish capacities.
Restraints
●Comparative efficacy vs newer platforms — inactivated vaccines often elicit less potent immune responses vs live-attenuated or mRNA (your content: “lesser efficacy”), which reduces perceived long-term competitiveness for some indications.
●Dose schedule & booster requirements — multiple doses/boosters can increase logistic complexity and reduce convenience.
●Dependence on legacy production (eggs) — supply constraints in avian supplies or biosecurity events can impact egg-based throughput.
Opportunities
●Cell culture and process modernization — increases scalability and reduces animal dependency (appeals to regulatory & social trends).
●Novel delivery systems (intradermal, patches, inhaled) — potential dose-sparing and improved uptake, opening new channels (retail, pharmacy).
●AI + digitalization — improves R&D speed, reduces batch failure risk and optimizes supply chain (see AI section).
●Online pharmacy & last-mile innovation — home delivery, tele-consultation bundling increases reach and convenience.
Key uncertainties / risks
●Vaccine hesitancy & geopolitical trade barriers — can affect uptake and export flows.
●Regulatory hurdles for new inactivated formulations — bridging studies and stability claims can delay market entry.
●Platform substitution risk (mRNA, viral vectors) — if broader indications shift to other platforms, demand growth could slow.
Top 10 companies

GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) — product/overview/strength
Overview: Global British pharmaceutical & vaccines leader with a large vaccines business and adjuvant experience.
Products / focus: Broad vaccine portfolio (influenza formulations, other routine vaccines) and strong adjuvant R&D.
Strengths: Global manufacturing footprint, regulatory experience, deep CMC and adjuvant platforms that enhance inactivated vaccine immunogenicity.
Sanofi Pasteur (Sanofi)
Overview: Sanofi’s vaccines arm (Pasteur) is a major global vaccine supplier with large influenza & combination vaccine capabilities.
Products / focus: Seasonal influenza, combination pediatric vaccines; active tech transfers to local producers (you cited an April 2024 transfer).
Strengths: Strong R&D, global supply/marketing reach, experience in complex combination vaccines.
Pfizer Inc.
Overview: Large U.S. pharma with major vaccine assets (Comirnaty, Prevnar historically with collaborations).
Products / focus: While known for mRNA with Comirnaty, Pfizer continues to be a top global vaccine developer and commercializer.
Strengths: Deep commercial reach, strong clinical development and regulatory track record.
Bharat Biotech International Ltd.
Overview: Hyderabad-based Indian vaccine innovator and manufacturer with many globally used vaccines (ROTAVAC, rabies, etc.).
Products / focus: Multiple licensed vaccines including inactivated vaccines (rabies, influenza lines).
Strengths: Strong domestic manufacturing, BSL-3 capability, proven global deliveries (billions of doses shipped per your content).
Serum Institute of India (SII)
Overview: World’s largest vaccine manufacturer by volume; heavy global supplier for routine immunizations and pandemic response.
Products / focus: Wide portfolio (influenza, DPT, MMR, etc.), large-scale fill-finish capacity.
Strengths: Unmatched volume capability, low-cost production, long WHO supply relationships.
Sinovac Biotech
Overview: Chinese biopharma focused on inactivated vaccines (CoronaVac was a high-profile whole-virus vaccine) and other routine vaccines.
Products / focus: CoronaVac (COVID-19, inactivated whole virus), Anflu (influenza).
Strengths: Strong domestic demand base, proven inactivated whole-virus vaccine experience and export capacity.
Johnson & Johnson (Janssen)
Overview: Large multinational with vaccine research and commercial capabilities (Janssen R&D arm).
Products / focus: Historically broad vaccines/biologics presence; strong contract manufacturing & global distribution networks.
Strengths: Global commercial reach and experience in large immunization programs.
Valneva SE
Overview: Specialty vaccine company focused on infectious disease vaccines, including whole-virus inactivated platforms. s: Specialty inactivated products (e.g., whole-virus COVID-19 vaccine VLA2001).
Strengths: Niche expertise in inactivated vaccines and European manufacturing footprint.
Merck & Co., Inc. (MSD)
Overview: Major U.S. pharma with deep vaccine R&D history (MMR, hepatitis contributions); strong global infrastructure.
Products / focus: Broad vaccine portfolio, R&D and supply chain experience.
Strengths: Historical vaccine innovation, large R&D resources and global manufacturing network.
Biological E. Limited
Overview: Indian biotech specializing in low-cost vaccine production and expanding into global prequalification-eligible products.
Products / focus: Large pipeline including OPV development and WHO prequalified products per your data.
Strengths: Low-cost manufacturing model, recent WHO prequalification successes opening procurement channels.
Latest announcements
Biological E. Limited — WHO prequalification for Oral Polio Vaccine Type 2 (August 2024)
●What happened: Biological E. received WHO prequalification for its novel OPV-2, which improves eligibility for UN procurement channels and helps eradicate poliovirus Type 2. UNICEF has already procured doses for distribution.
●Implication: Prequalification accelerates global procurement, increases revenue potential, and positions Biological E as an inactivated/oral vaccine exporter for polio campaigns.
Institute of Immunobiologicals & Sanofi — technology transfer (April 2024)
●What happened: A technology transfer agreement for domestic production of an acellular hexavalent vaccine — supporting national immunization supplies.
●Implication: Strengthens local manufacturing, shortens supply chains and reduces dependence on imports for combination vaccines.
Zydus Lifesciences — launch of VaxiFlu 4 (Feb 2025)
●What happened: Launch of a quadrivalent inactivated influenza vaccine providing coverage for four strains, aimed to reduce mismatch risk.
●Implication: Broader seasonal protection may raise uptake rates and reduce hospitalization risk in target populations; competitive landscape for flu vaccines intensifies.
Diosynvax Ltd. — pan-H5 vaccine positive results (Mar 2025)
●What happened: Computational biology-designed pan-H5 flu vaccine showed positive efficacy signals — a potential bridge between computational design and inactivated product candidates.
●Implication: Demonstrates how in silico design can feed faster antigen selection for inactivated formulations.
Industry commentary (Merck / Merck APAC expert quote)
●What happened: Senior industry experts emphasize that traditional vaccine types (including inactivated) will remain important due to regulatory track records & manufacturing investments.
●Implication: Reinforces the long-term relevance of inactivated vaccines despite newer platforms.
Recent developments
Portfolio refreshes (influenza quadrivalent, pan-H candidates) — companies are updating flu lineups (quadrivalent products) and exploring broadly protective H-type vaccines, reducing seasonal mismatch risk and boosting recurring demand.
Technology transfers & local production deals — stronger trend for national producers to license & domestically manufacture combination vaccines; this accelerates capacity expansion in Asia and lowers unit costs.
Regulatory wins (WHO prequalification) — prequalification opens access to large UN procurement budgets and export markets; Biological E. example shows this pathway to revenue expansion.
Manufacturing modernization — movement from egg-based dominance to more cell culture and single-use technologies; this aligns with the cell-culture segment being the fastest growing.
Digital & AI adoption in R&D/manufacturing — convergence of computational biology and ML-based process optimization (as with Diosynvax and others) points to efficiency gains in antigen design and batch yields.
Segments covered
By Vaccine Type
Viral vaccines (largest revenue share, 2024)
●Subpoints: Influenza (40–45% of viral sub-segment), rabies (fast grower), polio (high-growth projection).
●Explanation: Seasonal recurrence (influenza) drives volume; rabies and polio are campaign-driven with episodic procurement.
Bacterial vaccines
●Subpoints: Pertussis, typhoid — often toxoid/subunit but included in inactivated segments for some combinations.
●Explanation: Bacterial vaccines are more manufacturing-specific (toxoid production, conjugation) and often packaged in combination products.
By Technology / Production Process
Egg-based inactivated vaccines (55–60% in 2024)
●Subpoints: Legacy influenza production, cost-efficiency, limitations include egg allergies and slow scale-up.
●Explanation: Well-characterized, but less flexible for rapid scale shifts.
Cell culture-based inactivated vaccines (fastest growth)
●Subpoints: More scalable, animal-product free, attractive for ethical/vegan sentiment and supply resilience.
●Explanation: Enables faster ramp and more consistent yields, but CAPEX is higher.
By Route of Administration
●Intramuscular (dominant 60–65% in 2024) — standard for systemic immunogenicity.
●Intradermal (fastest growth) — skin’s antigen-presenting cells enable dose sparing and efficacy boosts; useful for rabies/BCG style strategies.
●Other (subcutaneous, nasal/inhaled, patches) — nasally delivered flu vaccines or patch prototypes aim to improve uptake & logistics.
By End-User / Distribution
●Hospitals — installed base, trained staff, vaccine cold chain and clinical oversight (dominant end-user).
●Research institutes — R&D & trials (fastest growth end-user).
●Hospital pharmacy / online / retail — hospital pharmacy dominant (45–50% distribution share in 2024), while online pharmacies are the fastest growth distribution channel.
By Geography / Region
(See regional insights section above — APAC dominance, North America R&D intensity, Europe specialty firms, LATAM/AF reliance on donors.)
Top 5 FAQs
Q1 — What exactly is an “inactivated vaccine” and why is it used?
A: An inactivated (killed) vaccine contains pathogens that have been grown and then killed or rendered non-replicating so they cannot cause disease — they stimulate immunity safely and are widely used for influenza, polio (IPV), rabies and others. They are particularly suitable for immunocompromised individuals because there is no risk of vaccine-derived infection.
Q2 — How big is the biological inactivated vaccine market and how fast will it grow?
A: Per the data you provided: USD 0.95B (2024) → USD 1.00B (2025) → USD 1.57B (2034 projected) with a CAGR of ≈5.14% for 2025–2034 (≈57% absolute growth across the period).
Q3 — Which region leads the market and why?
A: Asia-Pacific led in 2024 with ≈30–35% revenue share and is expected to grow fastest, driven by large immunization programs, population size, and major manufacturing hubs (India & China).
Q4 — What are the main technology/production splits?
A: Egg-based inactivated vaccines held the largest revenue share (55–60% in 2024) (legacy influenza capacity). Cell culture methods are the fastest-growing technology due to scalability and lower animal-product dependence.
Q5 — Who are the top manufacturers and what differentiates them?
A: Top firms include GSK, Sanofi Pasteur, Pfizer, Bharat Biotech, Serum Institute of India, Sinovac, J&J (Janssen), Valneva, Merck & Co., Biological E. Strengths vary: multinational R&D & adjuvant expertise (GSK), broad vaccine portfolios (Sanofi, Pfizer, Merck), large low-cost volume production (SII, Bharat Biotech, Biological E), and specialty inactivated expertise (Valneva, Sinovac).
Access our exclusive, data-rich dashboard dedicated to the therapeutic area sector – built specifically for decision-makers, strategists, and industry leaders. The dashboard features comprehensive statistical data, segment-wise market breakdowns, regional performance shares, detailed company profiles, annual updates, and much more. From market sizing to competitive intelligence, this powerful tool is one-stop solution to your gateway.
Access the Dashboard: https://www.towardshealthcare.com/access-dashboard
Immediate Delivery Available | Buy This Premium Research @ https://www.towardshealthcare.com/price/5932
Become a valued research partner with us – https://www.towardshealthcare.com/schedule-meeting
You can place an order or ask any questions, please feel free to contact us at sales@towardshealthcare.com
Powering Healthcare Leaders with Real-Time Insights: https://www.towardshealthcare.com/healthcare-intelligence-platform
Europe Region – +44 778 256 0738
North America Region – +1 8044 4193 44
APAC Region: +91 9356 9282 04
Web: https://www.towardshealthcare.com
Find us on social platforms: LinkedIn | Twitter | Instagram | Medium | Pinterest