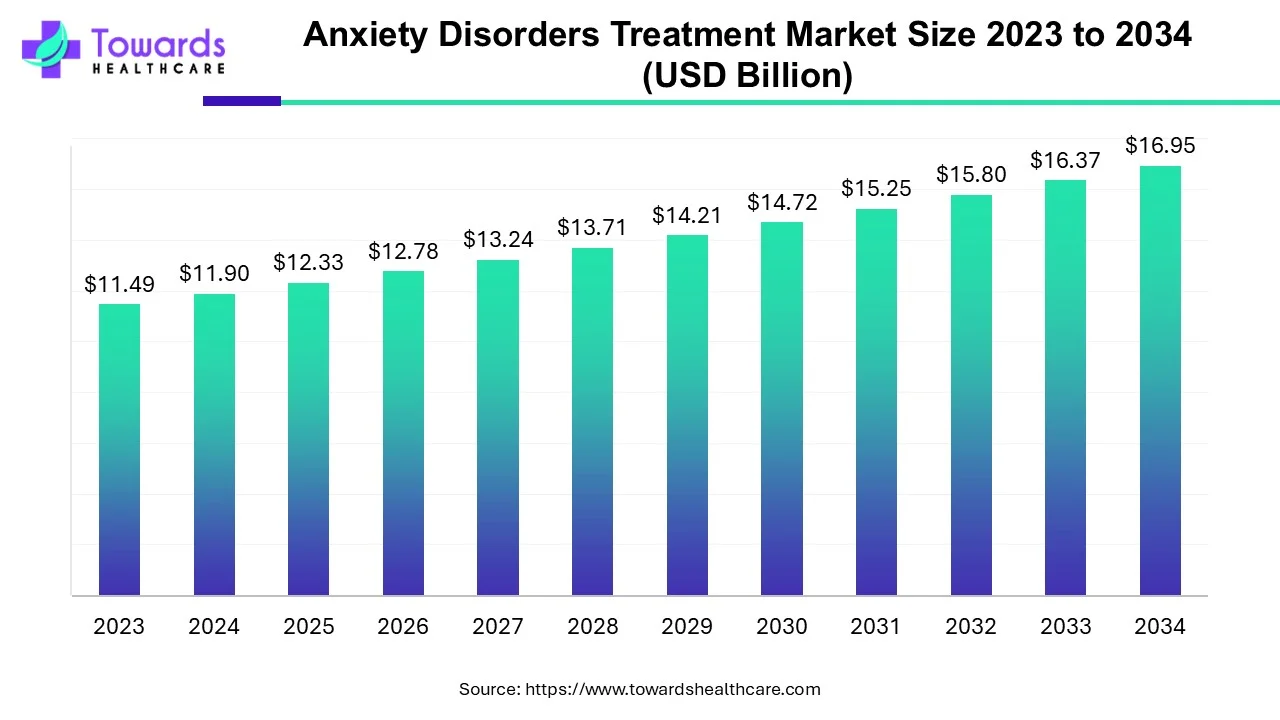
The global Anxiety Disorders Treatment market is forecast to grow from USD 12.33 billion in 2025 to USD 16.95 billion by 2034 — an increase of USD 4.62 billion over nine years, corresponding to a CAGR of 3.6% (2025–2034).
Download the free sample and get the complete insights and forecasts report on this market @ https://www.towardshealthcare.com/download-sample/5145
Market size (point-wise)
Key headline figures
◉2025 market size: USD 12.33 billion.
◉2034 market size (forecast): USD 16.95 billion.
◉Absolute growth (2025→2034): USD 4.62 billion (16.95 − 12.33 = 4.62).
◉Average annual absolute increase: ≈ USD 0.51 billion/year (4.62 ÷ 9 ≈ 0.513).
◉Compound annual growth rate (CAGR): 3.6%.
Important 2022 baseline shares (market structure anchors)
◉Disorder type: Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) held the largest share 34% in 2022.
◉Drug class (2022): SSRIs represented the largest drug-class share 32%.
◉Care setting (2022): Hospital outpatient settings dominated with a 71% share.
COVID-era & funding signals that affect market sizing and demand
◉Pandemic prescription spike: A 12% rise in Zoloft prescriptions was recorded in March 2020 (lockdowns, economic stress, social isolation cited as drivers).
◉Research funding (2015–2020): Approximately 76,000 grants from 345 funders across 38 countries — US$18.5 billion invested into mental-health research in that period (≈5% of registered grants; 4% of total research spend). 89% of these funds went to high-income countries and 39% of grants originated in the United States — this concentration shapes R&D and commercialization geography.
◉Digital adoption indicator: Global spending on wellness and mental-health apps rose markedly from 2019–2022 (user data in the brief points to rising investment and consumer spend in mobile/digital mental-health tools).
Market trends
1. Demand side trends
◉Post-COVID demand shock: The pandemic produced a measurable surge in anxiety and depression (e.g., March 2020 Zoloft prescriptions +12%), driving short-term and sustained demand for pharmacotherapy and remote therapy.
◉Growing mental-health awareness: Reduced stigma → more people seeking help → larger addressable market for meds, therapy and digital solutions.
◉Shift to outpatient care: Outpatient hospital settings held 71% of the market in 2022, reflecting preference for community-based and ambulatory management of anxiety (less inpatient care).
2. Treatment mix evolution
◉Pharmacotherapy still central: SSRIs (32% in 2022) retain the largest share among drug classes; benzodiazepines, SNRIs and others remain in use but face scrutiny (dependence risk, guideline shifts).
◉Therapy & hybrid models: CBT and other psychotherapies continue as first-line non-drug options; hybrid care (therapy + meds) grows, including combined digital CBT + pharmacotherapy programs.
◉Rise of digital therapeutics & apps: Investment and consumer spending on apps increased 2019–2022; pharma–digital partnerships (e.g., pharma working with digital CBT providers) are becoming common.
3. Supply side & industry structure
◉Competitive, multi-player landscape: Big pharma, generic manufacturers, specialty mental-health device/service firms, therapy clinic networks and digital-therapeutics startups all compete and collaborate.
◉R&D and M&A activity: Partnerships and consolidation—examples include pharma collaborations and corporate deals in 2020 (Neurocrine–Takeda; Big Rock Partners–NeuroRx). Regulatory approvals for new mechanisms (e.g., intranasal agents such as SPRAVATO) signal changing therapeutic mixes.
◉Funding concentration impacts innovation geography: 89% of mental-health grant funds went to high-income countries (2015–2020), skewing where R&D and clinical trials focus.
4. Access & workforce constraints
◉Shortage of mental-health professionals—especially child/adolescent specialists—constrains capacity, increases wait times, and boosts interest in telehealth and digital scaling solutions.
AI role and impact on the anxiety treatment market
1. Drug discovery & preclinical R&D
◉Role: Machine learning for target identification, compound screening and predicting molecule-target interactions.
◉Impact: Shortens early discovery timelines and reduces costs; increases the chance of novel anxiolytic mechanisms entering the pipeline (helps companies with limited R&D budgets punch above weight).
2. Clinical-trial optimization
◉Role: AI-driven patient-selection (predictive eligibility), adaptive trial designs, and digital biomarkers to improve signal detection.
◉Impact: Higher trial efficiency, lower drop-out, faster readouts — attractive in a market where new mechanisms (e.g., intranasal agents) are emerging and competition for trial participants is intense.
3. Screening, diagnosis & risk stratification
◉Role: Natural language processing (NLP) on clinical notes, voice/text analysis, and passive smartphone/ wearable data to flag anxiety patterns and predict escalation (e.g., panic attacks, suicidal ideation).
◉Impact: Earlier detection, triage prioritization (addresses workforce shortage), and personalization of care plans.
4. Personalized digital therapeutics & adaptive CBT
◉Role: AI personalizes CBT modules, pacing, and coping-strategy suggestions; reinforcement learning adapts content to engagement and symptom changes.
◉Impact: Better engagement, measurable outcomes from app-delivered therapy, potential to substitute or augment in-person CBT (scales access, fits outpatient dominance).
5. Virtual therapy assistants and clinician augmentation
◉Role: Conversational agents to provide between-session support, guided exposure exercises, or to assist clinicians with session notes and measurement-based care.
◉Impact: Reduces clinician burden, improves measurement frequency, and weakens the access bottleneck caused by professional shortages.
6. Remote monitoring & adherence
◉Role: Predictive models using passive sensor data (sleep, activity, social patterns) to trigger interventions or clinician alerts.
◉Impact: Improves medication adherence and therapy engagement, potentially lowering relapse/readmission and improving outpatient outcomes.
7. Real-world evidence & outcomes measurement
◉Role: Aggregate, anonymize and analyze patient-level outcome data from apps, EHRs and registries to demonstrate effectiveness for payers and regulators.
◉Impact: Facilitates reimbursement conversations for digital therapeutics and supports labeling claims for novel therapies.
8. Regulatory, ethical & operational constraints
◉Challenges: Data privacy, algorithmic bias, explainability, and clinical validation requirements. AI tools must meet clinical evidence thresholds to be accepted by clinicians, payers and regulators — this is a practical barrier to immediate, universal adoption.
9. Strategic market implication
Regional insights
North America
Urban concentration & outpatient leadership
◉Metro areas (NYC, LA, Toronto) concentrate specialists, research centers, and advanced clinics. This concentration reinforces outpatient dominance (71% share) and makes adoption of new treatments and digital programs faster in cities.
High funding & market liquidity
◉The U.S. accounted for 39% of mental-health grants (2015–2020), feeding R&D, trials and startup ecosystems (favors rapid commercialization).
Telehealth acceleration
◉Pandemic policy shifts made teletherapy widely accessible, reducing geographic access barriers and increasing the reach of digital therapeutics.
Europe
Regulatory complexity & opportunity
◉EMA pathways (e.g., acceptance of MAA filings such as Vyepti in neuro/neurology space) shape introduction of new products. National reimbursement variation creates both hurdles and pockets of rapid adoption.
Integrated community care models
◉Many European systems emphasize community/outpatient mental-health services, aligning with outpatient share dominance.
Asia Pacific
Cultural stigma & under-resourcing
◉Stigma around mental health in many countries depresses help-seeking, limiting market penetration despite rising need.
Rapid digital adoption but regulatory fragmentation
◉Mobile penetration and app use are high — ripe for digital therapeutics — but country-by-country regulation and reimbursement heterogeneity slow scale.
Workforce gap
◉Lower per-capita mental-health professionals intensifies demand for scalable AI and digital solutions.
Middle East & Africa
Infrastructure & access constraints
◉Limited specialist availability, patchy mental-health infrastructure and variable insurance coverage restrict market growth.
High unmet need
◉Stigma and resource constraints create an underserved opportunity for telehealth and low-cost digital interventions.
South America
Inequality in access
◉Urban centers have reasonable services; rural areas face shortages. Growth driven by private clinics, telehealth and regional generics producers.
Emerging payer interest
◉Growing recognition of productivity losses from untreated anxiety is prompting slow shifts toward coverage of outpatient care and digital tools.
Market dynamics
Key drivers
◉Rising prevalence and awareness — more patients seeking care.
◉Outpatient care preference — efficient, lower-cost care models (71% share).
◉Digital therapeutics & telehealth adoption — expands reach and reduces wait times.
◉Sustained pharma investment and collaborations — partnerships (e.g., pharma + digital CBT) accelerate combined offerings.
Principal restraints
◉Shortage of trained mental-health professionals — limits capacity for therapy and specialist consultations.
◉Funding concentration — heavy skew of research funding to high-income countries may limit innovation tailored for LMIC needs.
◉Regulatory hurdles & reimbursement gaps for digital therapeutics and newer drug classes.
Opportunities
◉AI & digital scaling — address workforce shortages and expand access to evidence-based therapy.
◉Novel mechanisms & regulatory openness — approval pathways for agents like intranasal therapies show regulators are receptive to new approaches for severe presentations.
◉Generics and cost-effective therapies — broadening access in price-sensitive markets (Teva and generics players).
Threats
◉Dependence and safety concerns with some drug classes (e.g., long-term benzodiazepine use).
◉Data privacy & trust issues around app/digital therapeutic data that could limit adoption.
◉Economic cycles — healthcare spending reprioritization could affect access and payer coverage.
Top companies
Pfizer Inc.
◉Products / relevance: Established presence in anxiolytic/antidepressant markets (Zoloft cited in content; March 2020 saw a 12% rise in prescriptions).
◉Overview: Global pharmaceutical leader with large commercial, regulatory and R&D capabilities.
◉Strengths: Massive distribution network; strong marketing and clinician relationships; capacity to pair drug launches with real-world evidence campaigns and digital partnerships.
Merck KGaA
◉Products / relevance: Broad life-science and specialty pharma activities that touch CNS therapeutic areas.
◉Overview: Diversified life-science and healthcare company with R&D focus.
◉Strengths: Integrated R&D and specialty manufacturing, enabling complex molecule development and supply.
Sanofi
◉Products / relevance: Established pharma with CNS and broad therapeutic interests.
◉Overview: Large multinational with global commercialization reach.
◉Strengths: Global market access, regulatory depth and experience managing large chronic-therapy portfolios.
Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS)
◉Products / relevance: Major pharma player with substantial R&D and M&A firepower.
◉Overview: Focus on innovative medicines; ability to pursue strategic partnerships in psychiatry and neuroscience.
◉Strengths: Deep R&D, M&A track record, and access to specialty clinical trial networks.
Eli Lilly
◉Products / relevance: Strong neuroscience R&D track record.
◉Overview: Large biotech/ pharma with pipeline emphasis on CNS agents.
◉Strengths: Innovation culture, clinical development expertise, and capabilities to bring novel psychiatric agents to market.
Teva Pharmaceutical Industries
◉Products / relevance: Generic manufacturer supplying broad antidepressant/anxiolytic portfolios.
◉Overview: World’s leading generics firm with scale in off-patent CNS medicines.
◉Strengths: Cost leadership, manufacturing scale, and distribution—critical for affordability and access.
Bayer AG
◉Products / relevance: Diversified healthcare presence including CNS/neurology linkages.
◉Overview: Large pharma/chemicals conglomerate with global reach.
◉Strengths: Cross-discipline R&D, industrial scale, and strong commercialization channels.
Biocare Medical, LLC
◉Products / relevance: Niche medical/diagnostic technologies supporting mental-health diagnostics and clinic equipment.
◉Overview: Smaller, specialized firm (listed among market companies).
◉Strengths: Specialized product focus, agility to serve clinician workflows and diagnostic labs.
GSK plc.
◉Products / relevance: Global pharma with historical CNS product experience.
◉Overview: Major multinational working across pharmaceuticals and vaccines.
◉Strengths: Large global footprint, regulatory expertise, and established clinician relationships.
Mitsubishi Chemical Group Corporation
◉Products / relevance: Chemical and life-science capabilities with interest in specialty pharmaceuticals and materials used in formulations.
◉Overview: Large industrial group with life-science subsidiaries.
◉Strengths: Manufacturing and materials science strengths; potential to support drug formulation and delivery innovations.
Latest announcements
◉Janssen + Koa Health collaboration (November 2020): Partnership to research digital CBT combined with pharmacological therapy for treatment-resistant major depressive disorder — shows pharma interest in combining drugs with validated digital therapeutics to improve outcomes and target non-responders.
◉FDA label expansion for SPRAVATO (August 2020): Janssen’s intranasal SPRAVATO added to oral antidepressant therapy for adults with major depressive disorder and acute suicidal ideation/behavior — signals regulatory acceptance of novel delivery mechanisms and rapid-acting agents relevant to severe mood/anxiety presentations.
◉Neurocrine + Takeda agreement (June 2020): Joint development work on innovative psychiatric disorder treatments — highlights cross-company collaboration to build psychiatric pipelines.
◉MAA acceptance for Vyepti (December 2020): Lundbeck’s MAA for Vyepti (CGRP inhibitor for migraine prevention) accepted by EMA — while migraine-focused, acceptance demonstrates regulatory momentum in neuro/behavioral therapeutic categories and potential cross-learning for anxiety treatments.
◉Big Rock Partners Acquisition Corp. + NeuroRx merger (December 2020): Corporate-finance activity indicating investor appetite for psychiatric/neurological therapy companies and for strategies that combine biotech and financial sponsors.
Recent developments
◉Pandemic accelerated both demand (prescription rises) and acceptance of remote/digital models.
◉Drug class dominance remains with SSRIs, but new mechanisms and formulations (e.g., intranasal agents) are being integrated into practice for severe cases.
◉Pharma–digital partnerships are increasing, with digital CBT being trialed in combination with drugs to reach treatment-resistant populations.
◉Research capital is concentrated in high-income countries, shaping where innovations and clinical trials occur and creating an uneven innovation geography.
◉Workforce shortages have intensified interest in telehealth, AI and digital therapeutics as scalable care options.
Segments covered
By Disorder Type
◉Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) 34% share in 2022. GAD represents the largest single disorder segment; chronic course and broad symptomatology drive consistent use of SSRIs, CBT, and long-term outpatient management.
◉Panic Disorder — episodic acute care needs; combination of meds and exposure-based therapy often used.
◉Agoraphobia — often co-occurs with panic disorder; treatment mixes CBT with pharmacotherapy and graded exposures.
◉Social Anxiety Disorder — increasing prevalence noted; therapy (group and CBT) and medications are common. Social-media and societal factors may be drivers.
Specific Phobia & Others — more niche but important in aggregate; exposure therapies are treatment mainstays.
By Treatment (deep subpoints)
◉SSRIs (32% share in 2022): First-line pharmacotherapy for many anxiety disorders — favorable safety profile relative to older classes.
◉SNRIs, TCAs, MAOIs, mixed antidepressants: Alternative antidepressant classes used when SSRIs fail or in comorbid depression; each has unique side-effect and monitoring profiles.
◉GABAergic drugs & benzodiazepines: Effective for short-term relief; dependence and tolerance concerns limit long-term use.
◉Antipsychotics / adjuncts: Used as augmentation in refractory cases.
◉Beta-blockers / antihistamines: Symptom-focused (e.g., somatic symptoms, performance anxiety).
◉Therapy (CBT and others): Evidence-based psychotherapies remain core; digital CBT scales access.
◉Other treatments: Digital therapeutics, mindfulness programs, and lifestyle interventions.
By Hospital Settings
◉Outpatient (71% share in 2022): Majority of care delivered here — aligns with chronic nature of many anxiety disorders and the suitability of outpatient therapy plus medication management.
◉Inpatient: Reserved for acute crises (e.g., suicidality, severe comorbidity) or complex cases requiring stabilization.
By Geography
◉North America / Europe / Asia Pacific / Middle East & Africa / South America — each region differs by care models, reimbursement, stigma levels, and workforce availability — explained previously in the Regional Insights section.
Top 5 FAQs
1) What is the expected market growth of the anxiety disorders treatment market?
Answer: The market is forecast to grow from USD 12.33 billion in 2025 to USD 16.95 billion by 2034, at a CAGR of 3.6% between 2025 and 2034.
2) Which disorder and drug class held the largest shares in 2022?
Answer: Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) was the largest disorder segment at 34% (2022); SSRIs were the largest drug class at 32% (2022).
3) How did COVID-19 affect anxiety treatment demand?
Answer: COVID-19 increased anxiety prevalence and treatment seeking (e.g., a 12% rise in Zoloft prescriptions in March 2020). The pandemic also accelerated telehealth and digital therapeutics adoption.
4) Where is most research funding concentrated and why does that matter?
Answer: From 2015–2020, US$18.5 billion went to mental-health grants (76,000 grants); 89% of funding was directed to high-income countries and 39% originated in the U.S. This concentration shapes where R&D, clinical trials and product launches are focused.
5) How are shortages of mental-health professionals shaping the market?
Answer: Workforce shortages (notably child/adolescent specialists) increase wait times and limit capacity for therapy, driving the market toward telehealth, digital therapeutics and AI-enabled solutions to scale access.
Access our exclusive, data-rich dashboard dedicated to the therapeutic area sector – built specifically for decision-makers, strategists, and industry leaders. The dashboard features comprehensive statistical data, segment-wise market breakdowns, regional performance shares, detailed company profiles, annual updates, and much more. From market sizing to competitive intelligence, this powerful tool is one-stop solution to your gateway.
Access the Dashboard: https://www.towardshealthcare.com/access-dashboard
Immediate Delivery Available | Buy This Premium Research @ https://www.towardshealthcare.com/price/5145
Become a valued research partner with us – https://www.towardshealthcare.com/schedule-meeting
You can place an order or ask any questions, please feel free to contact us at sales@towardshealthcare.com
Powering Healthcare Leaders with Real-Time Insights: https://www.towardshealthcare.com/healthcare-intelligence-platform
Europe Region – +44 778 256 0738
North America Region – +1 8044 4193 44
APAC Region: +91 9356 9282 04
Web: https://www.towardshealthcare.com
Find us on social platforms: LinkedIn | Twitter | Instagram | Medium | Pinterest