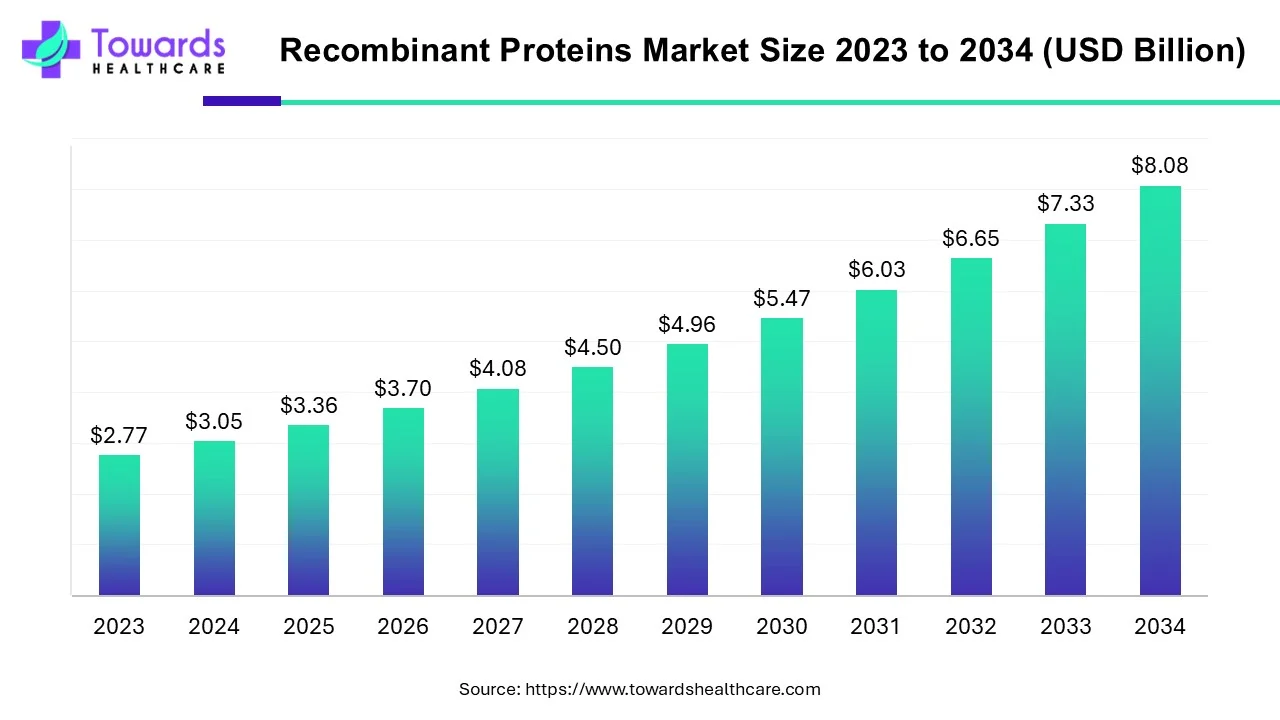
The global recombinant proteins market is valued at USD 3.36 billion in 2025 and projected to reach USD 8.08 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 10.24%. The market growth is driven by the rising incidence of chronic diseases (cancer, diabetes, autoimmune disorders), increasing demand for biologics and biosimilars due to patent expirations, the push for personalized medicines, and government initiatives supporting biotechnology R&D.
Download the free sample and get the complete insights and forecasts report on this market @ https://www.towardshealthcare.com/download-sample/5435
Market Size Insights
Global Growth (2025–2034)
◉2025: USD 3.36 billion
◉2034: USD 8.08 billion
◉CAGR: 10.24%
Regional Breakdown (2024 market share)
◉North America: 42% (largest share, led by U.S.)
◉Asia-Pacific: fastest growth, driven by R&D, government support, and biotech infrastructure.
◉Europe: growing due to personalized medicines and rising geriatric population.
Key Product Segments
◉Cytokines & Growth Factors: largest share in 2024, widely used in oncology, immunology, neurology.
◉Antibodies: projected to grow significantly due to demand in diagnostics and therapeutics.
Host Cell Systems
◉Mammalian Cells: dominant in 2024 due to high similarity to human proteins.
◉Bacterial Cells (E. coli): fastest growth due to easy handling and cost-efficiency.
Market Trends
Rising clinical & chronic disease burden → demand pull
◉Increasing cancer, diabetes, and autoimmune disorder prevalence creates sustained demand for recombinant therapeutics (e.g., immunostimulants, vaccines, antibodies, fusion proteins).
◉Implication: long-term, predictable demand that supports large CAPEX projects and multi-year supply contracts.
Patent expirations → biosimilars & biologic competition
◉Biologics patent cliffs open opportunities for biosimilars and lower-cost recombinant alternatives — driving competition, price pressure, but also larger addressable markets.
◉Implication: firms must balance price competition with differentiation (manufacturing quality, reliability).
Novel expression & production innovations
◉Non-traditional bioreactors and host systems (example: Loopworm’s work with silkworm bioreactors; $3.4M funding in 2024) show innovation toward alternative, potentially lower-cost production routes.
◉Implication: new host systems could reduce some costs or open niche applications (e.g., insect-derived post-translational modifications).
Large M&A and PE activity
◉ProGen acquisition (KKR & Bain, USD 950M) signals consolidation and strategic platform buys.
◉Implication: expect more rollups of specialized recombinant protein firms into platform companies; supplier rationalization and scaling advantages follow.
Corporate R&D scale-up
◉Example: Merck & Co. R&D spend jumped to ~USD 30B in 2023 (vs. USD 13.5B in 2022).
◉Implication: greater internal demand for research reagents and CMC (chemistry, manufacturing, controls) upstream work; faster pipeline development and more late-stage biologics candidate throughput.
Scale & capacity expansion by sample suppliers
◉Proteintech’s 2024 new UK facility (3× prior size) indicates capacity expansion to meet logistics, manufacturing and R&D demand.
◉Implication: improvements in lead-time and scale for reagents and custom protein projects.
Regulatory environment & approvals
◉With approx 100 recombinant therapeutic proteins approved by FDA (per supplied data), the regulatory precedent is mature but still complex — creating barriers to entry for therapeutic-grade production but enabling more standardized pathways.
Ongoing cost pressure & payer scrutiny
◉High production costs translate to high therapeutic pricing; this will trigger payer negotiation and possibly stricter cost-effectiveness scrutiny in some geographies.
Academic–industry collaborations
◉Partnerships like Pfizer CTI show a trend of industry leveraging academia for early innovation and then absorbing scale via industry channels.
◉Implication: a two-tier innovation model — academic discovery feeding industry scaling.
AI: Role & Impact on the Recombinant Proteins Market
In-silico protein design & structure optimization
◉Mechanism: ML models evaluate sequence→structure→function relationships to propose sequence variants with improved stability, binding or expression.
◉Business impact: shortens lead optimization, reduces failed constructs, increases probability of successful therapeutic candidates → lowers discovery costs and compresses timelines.
Expression system & host optimization
◉Mechanism: AI models correlate sequence, vector, host, and culture parameters to predict expression yield and solubility.
◉Business impact: faster selection of the optimal host (mammalian vs bacterial vs insect), fewer wet-lab iterations, higher yields at scale.
Bioreactor process control & predictive maintenance
◉Mechanism: real-time sensor data (pH, DO, temperature, optical density) fed into ML control loops to dynamically adjust feed rates, oxygenation, or temperature. Predictive maintenance flags equipment before failure.
◉Business impact: higher uptime, consistent yields, lower batch loss and downstream variability — improves cost per gram.
Downstream purification optimization
◉Mechanism: ML optimizes chromatographic steps and buffer conditions to maximize purity recovery and throughput.
◉Business impact: reduces number of purification cycles, improves overall process yield, lowers COGS for therapeutic grade proteins.
Analytics & quality control (QC)
◉Mechanism: ML/vision systems analyze mass spec, HPLC, electrophoresis and imaging data to detect subtle impurities or misfolding.
◉Business impact: more sensitive QC → fewer lot rejections and improved regulatory compliance; faster release cycles.
Predictive formulation & stability
◉Mechanism: algorithms predict excipient combinations and formulation conditions that maximize shelf life and thermal stability.
◉Business impact: reduced cold-chain dependence where possible, longer shelf life → lower distribution costs, broader geographic reach.
Candidate prioritization & in silico screening
◉Mechanism: AI triages millions of virtual variants for in vitro testing priority.
◉Business impact: better R&D resource allocation; smaller, higher-value wet-lab screening cohorts.
Patient stratification & personalized biologics
◉Mechanism: AI analyzes patient molecular data to identify those who will respond to a specific recombinant therapeutic.
◉Business impact: precision therapies with higher efficacy, enabling premium pricing and better clinical outcomes; supports personalized medicine business models.
Supply chain forecasting & demand planning
◉Mechanism: ML forecasts reagent and finished product demand using lead indicators (clinical readouts, regulatory milestones, sales trends).
◉Business impact: optimized inventories, just-in-time production, reduced stockouts and obsolescence.
Regulatory analytics & dossier automation (emerging)
◉Mechanism: NLP and structured data extraction streamline compilation of regulatory submissions and batch records.
◉Business impact: faster regulatory filing, lower submission cost, fewer errors in documentation.
◉Overall AI effect: compress R&D timelines, de-risk scale-up, increase yields/quality, and reduce operational cost drivers — collectively expanding addressable markets and enabling new product economics.
Regional insights
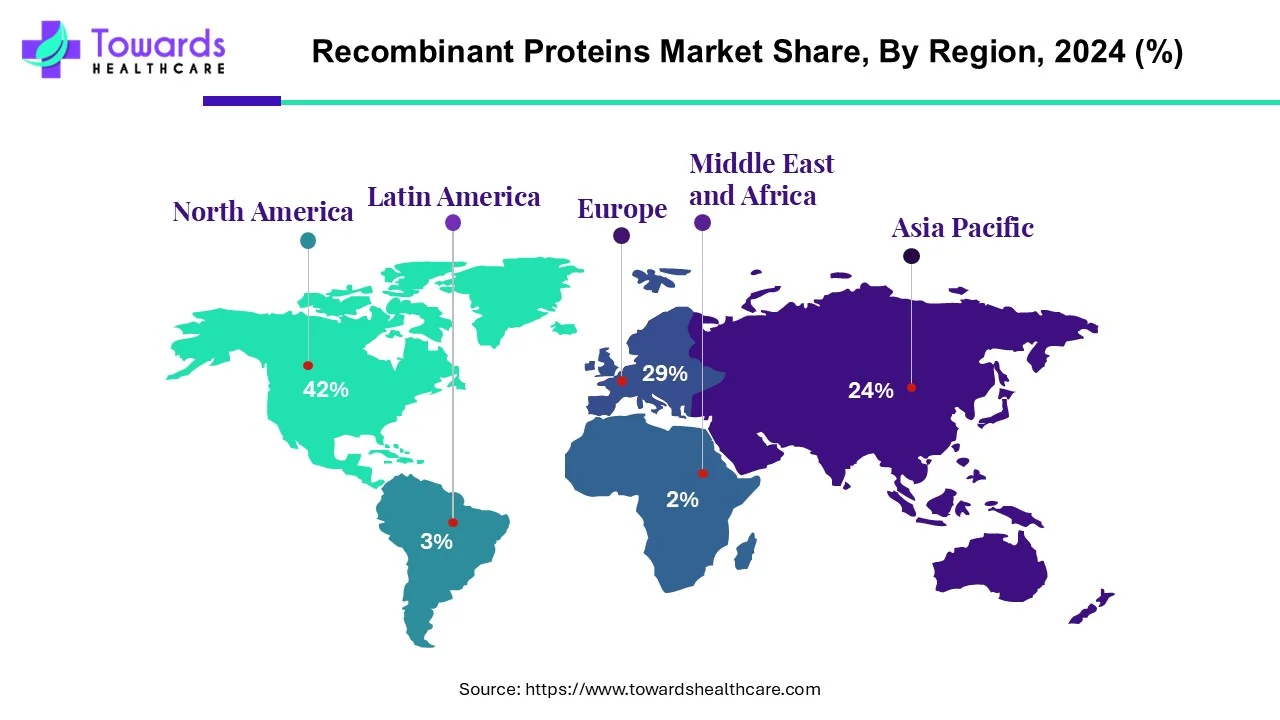
A. North America — (42% market share in 2024)
Demand & epidemiology
◉High cancer incidence (U.S. projected ~1.9M new cancer cases in 2024) drives oncology biologics demand.
Capital & R&D ecosystem
◉Concentrated biotech hubs (academic + VC + CMC suppliers) support rapid translation from discovery → scale.
Manufacturing & CMOs
◉Large existing biomanufacturing capacity and experienced contract manufacturers favor large-scale therapeutic production.
Regulatory clarity
◉Mature FDA pathways for recombinant biologics (≈100 approved) reduce regulatory uncertainty for new entrants.
◉Implication: North America is the primary commercial and clinical launch pad for high-value recombinant therapeutics and a target for early partnership/outsourcing.
B. Asia-Pacific — (highest projected CAGR)
Funding & government incentives
◉Growing public/private financing and favorable policies (cited generically) accelerate local R&D and manufacturing investments.
Scaling & cost arbitrage
◉Lower manufacturing costs and an expanding biotech workforce support scale manufacturing and exports.
Local innovation
◉Emerging alternative platforms (e.g., insect bioreactors) and localized production for regional needs.
◉Implication: APAC will be a growth and manufacturing hub — attractive for cost-sensitive large-volume products and biosimilars.
C. Europe — (significant growth)
Aging population & personalized medicine
◉Higher demand for personalized recombinant therapies and diagnostics; healthcare systems focus on outcomes.
Strong academic–industry collaboration
◉Dense research networks produce discovery pipelines that industry can commercialize.
M&A & strategic consolidation
◉Examples like Danaher’s acquisition of Abcam indicate consolidation to build end-to-end capabilities.
Implication: Europe will remain a strong innovation center and commercialization market for differentiated, high-value recombinant products.
D. Latin America & Middle East & Africa (emerging)
Growth potential but infrastructure gap
◉Countries like Brazil and South Africa show rising investment but overall manufacturing and cold-chain limitations constrain scale.
Government healthcare reforms
◉Improving healthcare budgets and procurement programs create windows for targeted market entry.
◉Implication: Opportunities for reagent supply, diagnostics and partnerships, but therapeutic launches require local manufacturing/partnership strategies.
Market dynamics (drivers, restraints, opportunities, threats, value chain)
Primary drivers
◉Disease incidence (cancer, diabetes, autoimmune) creating sustained therapeutic demand.
◉Patent expiries enabling biosimilars and new market entrants.
◉Large corporates and PE investment fueling capacity and platform purchases.
Key restraints
◉High production cost: production of clinical-grade recombinant proteins is capital- and resource-intensive — often described as “billions of dollars per kilogram” for therapeutic-grade material in your source, which restricts affordability and access.
◉Complex manufacturing & regulatory requirements: GMP facilities, validated processes, and rigorous QC are costly and time-consuming.
Opportunities
◉Biosimilars and cost-effective production routes (new host systems, process intensification).
◉AI-enabled design & manufacturing that reduces time-to-clinic and per-unit cost.
◉Outsourcing and CMO partnerships (e.g., Axio BioPharma opening up for manufacturing projects) expand capacity and shorten customer lead times.
Threats / challenges
◉Pricing/payer pressures that compress margins for expensive therapies.
◉Supply chain fragility for raw materials (media, resins, single-use disposables).
◉Technical risk: expression failures, low yields, or impurity profiles that can stall projects.
Value chain hotspots & levers
◉Upstream R&D — gene design, cell line engineering: high differentiation potential.
◉Upstream production — bioreactor strategy (batch/fed-batch/perfusion): primary cost driver for yield.
◉Downstream processing — chromatography and filtration: major cost and technical complexity.
◉Formulation & fill-finish — secure cold-chain and regulatory release: critical for final product viability.
◉Commercialization — pricing, reimbursement, and distribution channels determine market uptake.
Global healthcare production insights
◉Manufacturing stages — detailed
◉Gene & vector design: codon optimization and strong promoters influence expression.
◉Cell-line development: stable vs transient expression decisions affect timelines and per-batch economics.
◉Upstream cultivation: small-scale screening → scale-up in single-use or stainless steel bioreactors.
◉Downstream purification: capture (affinity), intermediate polishing (ion exchange, hydrophobic interactions), filtration, viral removal — these steps greatly affect cost and purity.
◉Formulation & fill-finish: sterile filling, lyophilization or liquid formulation; robust excipient selection for stability.
◉QC & release: structural analytics, potency assays, impurity profiling and sterility tests required for regulatory release.
Scale-up challenges & mitigation
◉Scalability of yields: a construct that expresses well at small scale may behave differently at 1,000–10,000 L. Mitigation: predictive modeling, process intensification, and pilot scale bridging.
◉Batch variability: process analytics and PAT (process analytical technology) help maintain consistency.
◉Downstream bottlenecks: chromatography resin capacity and throughput can constrain total output. Solution: continuous downstream processes, resin optimization.
CMO & outsourcing dynamics
◉Outsourcing to CMOs accelerates time-to-market and reduces up-front CAPEX; companies like Axio BioPharma positioning as partners signals greater market acceptance of outsourced recombinant manufacturing.
Quality & regulatory compliance
◉Therapeutic recombinant proteins require GMP facilities, validated processes, and extensive stability/safety data; this raises entry bar but protects incumbents who have validated platforms.
Logistics & distribution
◉Cold-chain dependency for many proteins increases distribution cost and complicates access in emerging geographies; formulation advances that reduce cold-chain reliance will expand reach.
Top companies (product / overview / strengths)

Thermo Fisher Scientific
Products: research reagents, protein expression systems, purification tools, analytical instruments, kits.
Overview: broad portfolio across research tools → manufacturing support.
Strengths: global distribution network, integrated instrument + consumable ecosystem, strong customer service & technical support.
Merck KGaA / Merck & Co.
Products: reagents, bioprocessing materials, therapeutic pipelines (Merck & Co.).
Overview: large pharma/chemical groups with vertical capabilities from reagents to therapeutics.
Strengths: massive R&D budgets (Merck & Co. R&D ~USD 30B in 2023), scale to invest in novel modalities and production platforms.
Bio-Techne
Products: cytokines, growth factors, antibodies, detection kits.
Overview: focused life-science reagents supplier with product depth in bioactive proteins.
Strengths: specialized catalog for research and translational applications; reputation for reagent quality.
Abcam plc
Products: antibodies, recombinant proteins, research reagents.
Overview: leading protein research tools supplier.
Strengths: FY2024 revenue reported between £475M–£525M (11.3%–13.4% CER CAGR since 2019). Strong catalogue breadth and academic penetration.
Abnova Corporation
Products: antibodies, recombinant proteins, assay kits.
Strengths: provides research reagents and custom services.
GenScript Biotech Corporation
Products: gene synthesis, custom recombinant proteins, antibody services.
Strengths: end-to-end gene → protein services, strong in custom and CRO offerings.
Sigma Aldrich Company
Products: broad reagent & consumable catalog across discovery and production support.
Strengths: global distribution and recognized brand for research reagents.
GE Healthcare
Products: bioprocessing systems, chromatography resins, analytical tools.
Strengths: infrastructure and instrument support crucial for large-scale biologics manufacturing.
Prospec-Tany Technogene Ltd. / BPS Bioscience / RayBiotech Life Inc.
Products: specialty recombinant proteins, assay reagents, cytokines, and kit solutions.
Strengths: niche product offerings for specific assay needs and translational research.
STEMCELL Technologies Inc. / Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
Products: cell culture systems, reagents, analytical instruments.
Strengths: strong presence in cell biology and research instrumentation.
Proteintech Group, Inc.
Products: antibodies, recombinant proteins.
Overview: expanding manufacturing footprint (new UK facility opened Mar 2024).
Strengths: increased in-house production capacity and logistics to support growing demand.
Sino Biological, Inc.
Products: recombinant proteins and antibodies with emphasis on infectious disease reagents.
Strengths: catalog breadth and capability for rapid response reagent production.
Note on company choices: strength descriptions focus on market roles (catalog breadth, manufacturing, R&D support, distribution). Use these as competitive positioning rather than precise financial rankings.
Latest announcements
◉Axio BioPharma (Sept 2024) — accepting recombinant protein manufacturing projects
What happened: Axio opened/upscaled manufacturing project intake.
Immediate impact: more options for companies seeking outsourced production; reduces lead times for R&D groups to move to pilot manufacturing.
Strategic implication: accelerates trend toward flexible outsourcing and CMO partnerships; increases market capacity and reduces entry friction for smaller biotech firms.
◉KKR & Bain acquisition of ProGen BioTech (Oct 2024) — USD 950M deal
What happened: major PE investment at a high revenue multiple (~7.2× FY2025 estimated revenue).
Immediate impact: signals investor appetite for recombinant protein platforms, especially those aligned with oncology and autoimmune therapeutics.
Strategic implication: more capital available for M&A, platform expansion, and scaling of manufacturing for therapeutic proteins.
◉Loopworm (Sept 2024 funding) — USD 3.4M to scale insect protein manufacturing and silkworm bioreactors in Bangalore
What happened: seed/early funding plus government incentives to scale an alternative bioreactor platform.
Immediate impact: validates alternative host research and could produce cost-effective production routes for non-mammalian proteins and certain reagents.
Strategic implication: diversification of host systems may open lower-cost niches (e.g., aquaculture feed, research proteins) and, if scaled, may be adapted for certain therapeutic or industrial proteins where glycosylation differences are acceptable.
Recent developments
Proteintech new UK facility (Mar 2024)
◉Details: new facility 3× larger than previous; integrated R&D, production, logistics, admin.
◉Consequences: better production lead times, capacity for larger custom projects, improved supply reliability for regional customers, and potential to serve both research and small-scale therapeutic production needs.
Danaher acquisition of Abcam (Aug 2023)
◉Details: Danaher agreed to buy Abcam for USD 24.00/share, valuing ~USD 5.7B (including debt/net adjustments).
◉Consequences: vertical integration of product portfolios (instruments + reagents), improved scale and distribution, potential R&D synergies, and competitive pressure on standalone reagents suppliers.
Market consolidation & financing activity (ProGen, KKR/Bain)
◉Consequences: elevated multiples reflect investor belief in recurring, high-margin business lines (custom protein manufacturing, platform technology). May accelerate roll-up strategies and platform investments.
Segments Covered in the Recombinant Proteins Market
By Product
◉Cytokines & Growth Factors
◉Description: Bioactive proteins that regulate immune responses, cell proliferation, and tissue repair.
◉Examples: Erythropoietin (EPO), Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (G-CSF), VEGF, NGF.
Use Cases:
◉Oncology: stimulate immune response against tumors.
◉Regenerative medicine: wound healing, stem cell proliferation.
◉Vaccines: act as immunostimulants.
◉Market Insight: Largest share in 2024 due to high adoption in oncology and immunology.
◉Implication: Consistent demand as they are required in both therapeutic formulations and cell culture production.
◉Interferons (IFNs)
◉Description: Recombinant proteins with antiviral, immunomodulatory, and antitumor properties.
◉Examples: IFN-α, IFN-β, IFN-γ.
Use Cases:
◉Viral infections: Hepatitis B and C, COVID-19 research.
◉Oncology: Used as adjuvant therapy in melanoma and leukemia.
◉Market Insight: Still widely used in oncology and virology, though competition from newer biologics is growing.
◉Implication: Remains a vital segment in infectious disease and oncology pipelines, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.
◉Interleukins (ILs)
◉Description: Cytokine family regulating communication between leukocytes and other cells.
◉Examples: IL-2, IL-6 inhibitors, IL-12, IL-15.
Use Cases:
◉Autoimmune disorders (RA, psoriasis).
◉Cancer immunotherapy (IL-2 in melanoma, renal cell carcinoma).
◉Cell therapy expansion (CAR-T cell culture supplements).
◉Market Insight: Strong growth from immuno-oncology pipelines.
◉Implication: Expansion tied to next-generation immunotherapies; IL-based drugs are being trialed in multiple cancer indications.
Antibodies (Recombinant mAbs & Fragments)
◉Description: Recombinant monoclonal antibodies and engineered fragments.
◉Examples: Trastuzumab biosimilars, anti-PD1/PD-L1 antibodies, recombinant scFvs.
◉Use Cases:
◉Therapeutics: checkpoint inhibitors, oncology drugs.
◉Diagnostics: immunoassays, ELISA, IHC.
◉Research reagents.
◉Market Insight: Fastest-growing product category due to increasing approvals of therapeutic antibodies and biosimilars.
◉Implication: Antibody segment will dominate revenue growth, as therapeutic antibodies remain the single largest class of biologics globally.
By Host Cell System
◉Mammalian Cell Expression Systems
◉Description: Use of CHO (Chinese Hamster Ovary) cells, HEK293, and other mammalian cell lines.
◉Advantages: Human-like post-translational modifications, high protein fidelity.
Use Cases:
◉Therapeutic-grade protein production (antibodies, hormones, cytokines).
◉Complex proteins requiring glycosylation.
◉Market Insight: Largest share in 2024, gold standard for therapeutic biologics.
◉Implication: High CAPEX/OPEX but essential for therapeutic-grade proteins; will continue as industry backbone.
◉Bacterial Cell Expression Systems
◉Description: Mainly E. coli for high-yield expression.
◉Advantages: Low cost, rapid growth, scalable fermentation.
Use Cases:
◉Production of simple proteins, enzymes, and research reagents.
◉Biosimilars and industrial proteins.
◉Market Insight: Fastest growth projected due to cost efficiency and process familiarity.
◉Implication: Attractive for biosimilars, diagnostics, and developing market supply.
◉Yeast Expression Systems
◉Description: Pichia pastoris, Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
◉Advantages: Low cost, eukaryotic processing, moderate glycosylation.
Use Cases:
◉Enzymes, hormones, industrial proteins.
◉Some vaccine antigens (e.g., hepatitis B vaccine).
◉Market Insight: Growing adoption for mid-complexity proteins.
◉Implication: Could bridge cost–quality gap between bacterial and mammalian systems.
◉Insect Cell Expression Systems
◉Description: Baculovirus expression in insect cells (e.g., Sf9, silkworm).
◉Advantages: Post-translational modifications closer to mammalian than yeast; scalable.
Use Cases:
◉Vaccines, recombinant enzymes, structural proteins.
◉Novel applications: silkworm bioreactors (Loopworm).
◉Market Insight: Early-stage innovation but gaining attention with alternative bioreactors.
◉Implication: Potential to reduce cost of complex proteins if scaled effectively.
By Application
◉Drug Discovery & Development
◉Description: Recombinant proteins used as drug targets, reagents, and assay tools.
◉Examples: Kinases, growth factors, cytokines.
◉Market Insight: Core demand from pharma R&D labs.
◉Implication: Scales directly with R&D spending (e.g., Merck’s USD 30B in 2023).
◉Therapeutics & Clinical Use
◉Description: Recombinant proteins as active therapeutic agents.
◉Examples: Insulin, erythropoietin, interferons, recombinant antibodies.
◉Market Insight: Fastest revenue-generating segment; oncology dominates.
◉Implication: High-margin segment, but regulatory and pricing pressures are intense.
◉Industrial & Specialty Use
◉Description: Enzymes, proteins for diagnostics, specialty reagents.
◉Examples: Enzyme reagents for PCR, CRISPR proteins, diagnostic antigens.
◉Market Insight: Stable but less high-growth.
◉Implication: Attractive for SMEs and niche suppliers.
By End User
◉Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies
◉Usage: Therapeutics, biosimilars, and pipeline R&D.
◉Implication: Largest revenue driver, accounts for bulk demand.
◉Academic & Research Institutes
◉Usage: Fundamental biology, translational research, assay development.
◉Implication: Smaller in revenue, but critical for discovery and early-stage pipelines.
◉Contract Research & Manufacturing Organizations (CROs/CMOs)
◉Usage: Outsourced protein production, scale-up, GMP manufacturing.
◉Implication: Fastest growth in end-user segment due to outsourcing trend.
5 Top Searched Queries
1. What is the current size of the recombinant proteins market?
The global recombinant proteins market is valued at USD 2.88 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow steadily.
2. What is the forecasted growth rate of this market?
The market is expected to expand at a CAGR of 11.24% from 2025 to 2034, reaching significant levels.
3. Which regions dominate the recombinant proteins market?
North America leads due to strong biotech investments, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific with rising demand.
4. What drives the demand for recombinant proteins?
Growing applications in drug development, vaccines, and research are the key growth drivers.
5. Who are the key players in the recombinant proteins market?
Major players include Thermo Fisher Scientific, Merck KGaA, Bio-Rad, and Abcam among others.
Access our exclusive, data-rich dashboard dedicated to the healthcare market – built specifically for decision-makers, strategists, and industry leaders. The dashboard features comprehensive statistical data, segment-wise market breakdowns, regional performance shares, detailed company profiles, annual updates, and much more. From market sizing to competitive intelligence, this powerful tool is one-stop solution to your gateway.
Access the Dashboard: https://www.towardshealthcare.com/access-dashboard
Immediate Delivery Available | Buy This Premium Research @ https://www.towardshealthcare.com/price/5435
Become a valued research partner with us – https://www.towardshealthcare.com/schedule-meeting
You can place an order or ask any questions, please feel free to contact us at sales@towardshealthcare.com
Europe Region – +44 778 256 0738
North America Region – +1 8044 4193 44
Web: https://www.towardshealthcare.com
Find us on social platforms: LinkedIn | Twitter | Instagram | Medium | Pinterest