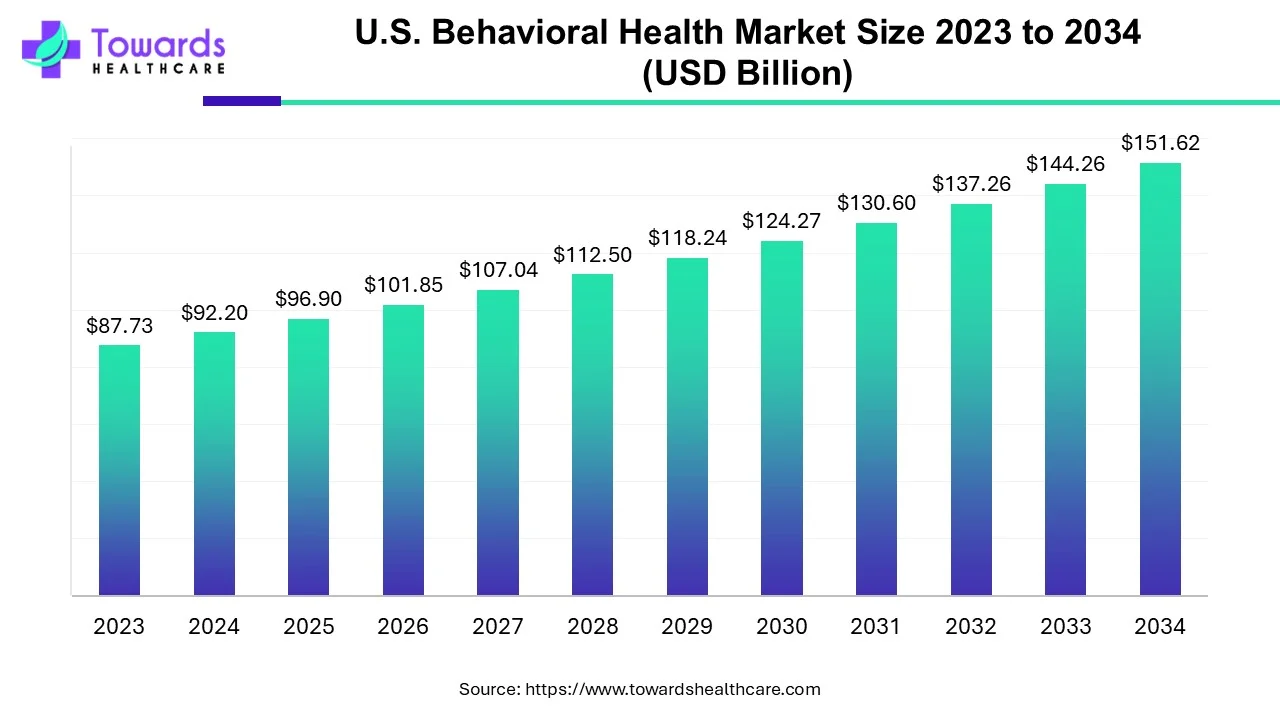
The U.S. behavioral health market was USD 92.2 billion in 2024, is projected at USD 96.9 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 151.62 billion by 2034 — a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.1% (2024–2034).
Download the free sample and get the complete insights and forecasts report on this market @ https://www.towardshealthcare.com/download-sample/5007
Market size
Key headline numbers & math
◉Base & projection: 2024 = USD 92.2B → 2025 = USD 96.9B → 2034 = USD 151.62B (given).
◉The projection is consistent with the formula: 92.2 × (1.051)^10 ≈ 151.62.
◉Absolute growth (2024→2034): USD 59.42 billion increase (151.62 − 92.2 = 59.42).
◉Doubling time at 5.1% CAGR: ≈ 13.9 years (ln2 / ln1.051 ≈ 13.93 years) — so the market will not double within the 10-year window, but will grow 64.4%.
Year-by-year (modelled at constant 5.1% CAGR from 2024)
◉2024 — 92.20 B (base)
◉2025 — 96.90 B (given / 92.20 × 1.051)
◉2026 — 101.84 B
◉2027 — 107.04 B
◉2028 — 112.50 B
◉2029 — 118.23 B
◉2030 — 124.26 B
◉2031 — 130.60 B
◉2032 — 137.26 B
◉2033 — 144.26 B
◉2034 — 151.62 B (target)
Market trends
Macro / policy & funding trends
◉Favorable government support: continued federal initiatives and funding are major growth drivers (SAMHSA funding, White House national strategy).
◉Example: SAMHSA announced USD 46.8M (May 2024) for youth mental health, workforce, substance use treatment and TTA (Minority Fellowship Program funding).
◉SAMHSA’s 2025 updated National Behavioral Health Crisis Care Guidance (policy guidance for states/tribes/localities) is a structural input expected to shape crisis care investments and operations.
◉White House national mental health/substance use strategy (2024): pushes coordination and resources, encouraging system redesign and payer/policy changes.
Market structure & care-delivery trends
◉Outpatient counseling dominance (2024): outpatient counseling held the largest share of services in 2024 — driven by lower cost, larger provider pool, and preference for ambulatory care for mild–moderate disorders.
◉Home-based treatment acceleration: home-based and telehealth services are expanding rapidly and are projected to grow fastest among service types. COVID-era telehealth adoption accelerated payer and provider acceptance.
◉Shift away from inpatient: inpatient share has declined (historical inpatient hospital treatment was 22.0% in 2020 in one dataset), with movement toward outpatient, homecare, and community settings.
◉Substance abuse disorder growth: substance use disorders are a high-growth disorder segment — 17.82% of adults (~45M people) had a substance use disorder in 2024 (per given data), driving demand for addiction treatment and rehab capacity expansion.
◉Workforce shortages: severe shortages forecast for counselors, psychiatrists, psychologists and social workers; >112 million Americans live in areas with a dearth of mental-health providers — a structural constraint on capacity.
◉Payer strategy and payment reform: payers experimenting with integrated care, value-based reimbursement, and outcome measures (example: Blue Shield of North Carolina/Blue Cross examples mentioned) to improve access and quality.
◉Private investment & digital entrants: VC / equity funded digital health firms and platforms (example: BeMe Health’s $12.5M Series A — Aug 2024) are adding new tele-and-digital options.
Company / ecosystem collaboration trends
◉Public-private collaboration & consolidation: more strategic partnerships (e.g., Arbital Health + Quartet Health — Oct 2024) and integration efforts to coordinate specialty mental health with primary care and population health.
◉Knowledge / measurement focus: pushes for measurement-based care remain, but provider adoption lags due to tech and workflow gaps.
AI’s role & impact
1) Screening, triage & access optimization
◉Automated large-scale screening: ML models analyze questionnaires, EHR history and passive signals (app/wearable data) to prioritize patients for clinician review.
◉KPI examples: reduction in time-to-first-contact, increased triage sensitivity, decreased inappropriate ER referrals.
◉Dynamic triage routing: AI decides appropriate care level (self-help / coach / outpatient / intensive) by scoring risk in real time.
2) Digital therapeutic delivery & augmentation
◉Conversational agents / digital coaches: AI chatbots provide scaled CBT/behavioral coaching, crisis text triage, and 24/7 support to reduce unmet need.
◉Role: symptom monitoring, prompting safety plans, augmenting therapy between visits.
◉Hybrid clinician-AI workflows: clinicians use AI summaries, suggested interventions, and structured progress reports — improving session efficiency and measurement-based care uptake.
3) Personalization & treatment optimization
◉Precision treatment matching: ML matches patients to therapeutic modalities, clinicians, or programs (e.g., intensity level, psychotherapy style) given history and predicted response patterns.
◉Medication management support: predictive models flag likely nonresponse or adverse reactions, assisting psychiatrists in medication choices and monitoring.
4) Digital phenotyping & remote monitoring
◉Sensors & wearables: physiologic and behavioral signals (sleep, mobility, heart rate variability) feed ML models to detect deterioration or relapse risk in real time; enables preemptive outreach.
◉Passive data analytics: smartphone usage patterns and voice/text signal analysis used to detect mood shifts — with consent and privacy protections required.
5) Outcomes prediction, population health & operations
◉Outcome forecasting: models predict hospitalization, relapse, or readmission risk to allocate case management resources.
◉Operational impacts: reduces preventable admissions, optimizes care management caseloads.
◉Capacity planning & workforce optimization: predictive analytics optimize staffing and clinic schedules and identify geographic shortage hotspots.
6) Quality measurement & value-based payment enablement
◉Automated measurement reporting: NLP + structured data collection generates standardized quality metrics (PHQ-9 trends, remission rates) for payers and value contracts.
◉Attribution & fraud detection: AI assists payers in validating claims and detecting anomalous patterns, improving integrity of reimbursement.
7) Provider productivity & administrative relief
◉Documentation automation: AI generates visit notes, coding suggestions and billing support, reducing administrative burden and improving clinician retention.
◉Clinical decision support (CDS): evidence-based recommendations surfaced at the point of care to standardize quality.
8) Implementation & governance considerations (risks/controls)
◉Bias & fairness: model bias risks exist (historical under-diagnosis in minority groups). Rigorous validation, stratified performance metrics, and ongoing monitoring are mandatory.
◉Privacy & consent: sensitive behavioral health data demands strict consent models, de-identification, and secure data governance.
◉Explainability & clinician trust: black-box models reduce uptake; tools must prioritize explainable outputs and clinician oversight.
◉Regulatory & reimbursement alignment: reimbursement models and FDA/CMR guidance influence which AI tools scale in clinics.
Regional insights
1) Urban / metropolitan regions
◉Provider concentration & specialty services: major metros house more psychiatrists, specialty clinics and integrated care networks; higher availability of outpatient counseling and rehab centers.
◉Higher digital adoption: denser broadband and greater provider digital-health adoption facilitate hybrid models and specialist teleconsults.
2) Rural & underserved areas
◉Acute provider shortage: over 112M Americans are in areas lacking adequate mental-health provider supply — rural areas are disproportionately affected.
◉Consequences: higher unmet need, longer wait times, greater reliance on primary care and emergency services.
◉Telehealth as an enabler: rapid telehealth expansion reduces travel barriers and extends specialty access, but broadband/infrastructure and reimbursement parity remain limiting factors.
3) State policy / Medicaid differences
◉Medicaid optional services create variability: states decide optional coverage for rehab, therapy, peer support and IMD coverage — produces uneven access and geographic inequity.
◉IMD (Institutes for Mental Disease) rules: variability in whether states cover IMD services for younger populations can limit adolescent access in some states.
4) Payer mix & Medicare impact
◉Medicare beneficiaries and severe illness: Medicare enrollees show a relatively higher prevalence of severe mental illness; Medicare coverage rules (e.g., 190-day inpatient cap historically) can constrain long-term inpatient access.
◉Commercial payer innovation: commercial insurers in certain states are piloting value-based behavioral health models (payer-led initiatives noted in source), accelerating integrated care where implemented.
5) Facility distribution & capacity
◉Facility count: there were 15,424 Mental Health & Substance Abuse Clinics in the U.S. (2023) — but distribution is uneven; states/regions differ in per-capita capacity and facility type mix (outpatient vs inpatient vs rehab).
Market dynamics
Drivers
◉Policy & funding: federal strategy, SAMHSA grants, and new crisis-care guidance drive investment and service expansion.
◉Epidemiology: rising prevalence of depression, anxiety and substance use disorders (e.g., anxiety represents a leading share; substance use 17.82% adult prevalence in 2024).
◉Technology & telehealth: telehealth and digital care lower access barriers and enable home-based treatment expansion.
◉Payer innovation: increasing experiments with value-based reimbursement and payer-provider partnerships to integrate behavioral health.
Restraints
◉Coverage gaps & parity enforcement issues: MHPAEA requires parity in benefit levels but does not mandate coverage; enforcement and parity remain imperfect — many insured people still lack comparable behavioral-health coverage.
◉Medicare/Medicaid limits: state discretion in Medicaid optional services, IMD rules, and Medicare historical inpatient limits (190-day cap) restrict access to certain services.
◉Poor reimbursement & undervaluation: mental-health clinician reimbursement remains low (example: psychiatrists reimbursed ~20% less than primary care — given in source), discouraging provider supply.
◉Workforce shortages: shortages of psychiatrists, psychologists, counselors, social workers and specialized professionals limit capacity.
Opportunities
◉Payer-based strategy & measurement: payers can drive system transformation by integrating care, deploying point solutions at scale, quantifying outcomes and increasing value-based reimbursement (Blue Shield NC example).
◉Home-based & digital growth: homecare settings forecasted to grow fastest (homecare CAGR: 9.55% for 2021–2027 in the end-user table), unlocking consumer preference–led growth.
◉Substance use disorder care expansion: high prevalence creates a large addressable market for rehab, medication-assisted treatment, and digital support tools.
◉Workforce leverage via AI & task-shifting: technology can augment existing workforce, allow lower-cost providers to manage stable patients, and extend reach.
Top companies

1. Acadia Healthcare
◉Overview / products: Large national behavioral-health provider network offering inpatient psychiatric hospitals, outpatient clinics, and addiction treatment services.
◉Strengths: Scale and geographic reach; ability to operate high-intensity inpatient and extensive outpatient networks; leverage nationwide referral pathways.
2. Universal Health Services (UHS)
◉Overview / products: Broad healthcare system with behavioral health divisions operating acute psychiatric hospitals, residential programs and associated outpatient services.
◉Strengths: Integrated hospital-operating expertise, cross-referral from general hospitals, financial scale for capital investments.
3. Behavioral Health Group, Inc.
◉Overview / products: Provider of behavioral health services including outpatient programs, community-based care and disorder-specific programs.
◉Strengths: Community orientation; agility in launching localized programs and partnerships.
4. Epic Health Services (Aveanna Healthcare)
◉Overview / products: Home health and behavioral-health provider services, emphasizing in-home care and community services.
◉Strengths: Expertise in home-based delivery and pediatric behavioral health; capacity to scale homecare modalities.
5. Ardent Health Services & CRC Health Group
◉Overview / products: Operators of acute hospitals and specialty behavioral health programs, including addiction and rehabilitation services.
◉Strengths: Combination of acute care experience and specialty rehab program management; operational integration.
6. IBH Population Health Solutions
◉Overview / products: Population health and care-management services focused on behavioral health integration and care coordination.
◉Strengths: Focus on outcomes, care coordination and payer/provider integration — useful in value-based contracts.
7. CuraLinc Healthcare
◉Overview / products: Employee assistance, workplace behavioral health, and managed behavioral health services.
◉Strengths: Employer-facing programs and workplace mental health solutions; strong engagement channels with payers/employers.
8. North Range Behavioral Health
◉Overview / products: Regional behavioral health system providing community mental health, crisis services and outpatient care.
◉Strengths: Local/regional leadership and community alignment; crisis services expertise.
9. Promises Behavioral Health (Elements Behavioral Health)
◉Overview / products: Addiction treatment, residential programs and recovery services.
◉Strengths: Reputation in addiction treatment and residential rehab; structured program offerings.
Latest announcements
◉Arbital Health + Quartet Health (Oct 2024): Long-term strategic collaboration to support Quartet’s mental-health program aimed at cost reduction and improved outcomes for serious mental-illness populations.
◉Implication: further integration of specialty behavioral health with value-based population management and digital triage/coordination services.
◉SAMHSA funding (May 2024 — USD 46.8M): Targeted funding for youth mental health, workforce expansion, substance use treatment and training/technical assistance (Minority Fellowship Program component).
◉Implication: targeted workforce pipeline strengthening and support for under-served populations; short-to-medium term boost to capacity.
◉BeMe Health Series A (Aug 2024 — USD 12.5M): Funding to improve age-specific support content and interactive tools to maintain youth mental wellness.
◉Implication: continued growth in youth-focused digital services and content personalization.
◉Surgo Health — Youth Mental Health Tracker (Dec 2024): Platform launched in partnership with Pivotal and SHOWTIME/MTV to aggregate youth mental health & wellbeing data across the U.S.
◉Implication: improved population surveillance and targeted program design for youth interventions.
◉NextGen Healthcare Center of Innovation (July 2024): Center launched with Mental Health Corporations of America to promote best practices and education in behavioral healthcare delivery.
◉Implication: emphasis on best practice dissemination and provider education to accelerate quality improvement.
Recent developments
◉Data & measurement emphasis: new databases/trackers (Surgo Youth Mental Health Tracker) and COIs indicate growing investment in population surveillance and best-practice sharing — foundation for measurement-based care.
◉Funding into workforce & youth care: SAMHSA grants and philanthropic/VC funding (BeMe) create near-term resource inflows to address workforce and youth engagement gaps.
◉Strategic platform partnerships: Arbital + Quartet exemplifies cross-company collaboration to scale mental-health programs across payers and provider networks — pushing toward integrated population care.
◉Provider & payer experimentation: payer initiatives (value-based pilots) plus new centers of innovation suggest the market is at a transition point from fee-for-service fragmentation toward outcome orientation — though reimbursement and parity remain limiting.
Segments covered
By Service Type (what each includes and growth drivers)
Outpatient Counseling
◉Includes: individual & group psychotherapy, outpatient psychiatric medication management, day programs delivered in clinics or via telehealth.
◉Drivers: cost-efficiency, patient preference, large provider pool, flexibility; currently dominant share.
Home-Based Treatment Services
◉Includes: home visits, mobile crisis teams, teletherapy, remote monitoring, in-home medication management.
◉Drivers: telehealth expansion, patient preference for home care, technology (apps, wearables); forecasted fastest growth.
Emergency Mental Health Services
◉Includes: ED psychiatric assessment, crisis stabilization units, mobile crisis response.
◉Drivers: acute incidents, insufficient community alternatives; policy focus on crisis care guidance (SAMHSA 2025).
Inpatient Hospital Treatment
◉Includes: acute psychiatric hospitalization, specialized inpatient units for severe mental illness and intensive detoxification/withdrawal.
◉Drivers/limits: necessary for high acuity but constrained by capacity, reimbursement, and a general shift toward less-restrictive settings.
Intensive Care Management
◉Includes: assertive community treatment (ACT), intensive outpatient programs (IOP), case management for high-risk patients.
◉Drivers: need to reduce readmissions and manage severe/chronic cases in community settings.
By Disorder Type (implications & care pathways)
Depression & Anxiety Disorder
◉Prevalence & impact: held the highest share in 2024; primary drivers of outpatient volume.
◉Care pathway: screening → outpatient psychotherapy & meds → stepped care including IOP if needed.
Substance Abuse Disorder
◉Prevalence & impact: rapid expansion projected; ~17.82% adult prevalence in 2024.
◉Care pathway: detox/medical management → inpatient/residential rehab → outpatient counseling & recovery supports / MAT.
Bipolar Disorder
◉Care pathway: pharmacotherapy, psychoeducation, ongoing outpatient psych management, and crisis stabilization as needed.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
◉Care pathway: trauma-focused therapies (e.g., exposure therapies), medication management, peer support.
Eating Disorder
◉Care pathway: multidisciplinary (medical, nutritional, psychotherapy), often requiring partial hospitalization or residential care for severe cases.
Others
◉Includes: ADHD, autism-related behavioral supports (if behavioral health scope includes), personality disorders — varying intensity and specialist involvement.
By End-User (who receives services and trends)
Outpatient Clinics
◉Share: largest end-user share historically (36.9% in 2020 in one dataset).
◉Trend: continued growth as primary access point for mild–moderate disorders.
Homecare Setting
◉Trend & CAGR: fastest growth (homecare CAGR 9.55% for 2021–2027 in one dataset); propelled by telehealth and patient preference.
Hospitals
◉Role: acute stabilization, high acuity inpatient stays; growth slower due to shift to outpatient/homecare.
Rehabilitation Centers
◉Role: addiction rehab and structured residential recovery services; steady growth driven by SUD prevalence.
Top 5 FAQs
1. What is the current size and projected growth of the U.S. behavioral health market?
Answer: The market was USD 92.2B in 2024, forecast to be USD 96.9B in 2025, and USD 151.62B by 2034, growing at a 5.1% CAGR (2024–2034).
2. Which service segments are growing fastest?
Answer: Home-based treatment services are projected to grow fastest (post-COVID trends and telehealth adoption). Outpatient counseling remains the largest single segment by share.
3. What are the main constraints on market growth?
Answer: Key restraints include coverage gaps / inadequate parity enforcement (MHPAEA limitations), poor reimbursement (mental-health clinician rates 20% lower than primary care in the source), and workforce shortages in many regions.
4. How will AI and digital health affect this market?
Answer: AI will expand scaled screening/triage, digital CBT/chatbots, remote monitoring via wearables, precision treatment matching, outcome prediction and administrative automation — improving access and efficiency but requiring robust governance for fairness and privacy.
5. What are the major near-term policy and funding developments to watch?
Answer: SAMHSA’s funding injections (e.g., USD 46.8M in May 2024) and 2025 National Behavioral Health Crisis Care Guidance, plus the 2024 White House national strategy, are key drivers for workforce funding, crisis care expansion and system redesign.
Access our exclusive, data-rich dashboard dedicated to the healthcare market – built specifically for decision-makers, strategists, and industry leaders. The dashboard features comprehensive statistical data, segment-wise market breakdowns, regional performance shares, detailed company profiles, annual updates, and much more. From market sizing to competitive intelligence, this powerful tool is one-stop solution to your gateway.
Access the Dashboard: https://www.towardshealthcare.com/access-dashboard
Immediate Delivery Available | Buy This Premium Research @ https://www.towardshealthcare.com/price/5007
Become a valued research partner with us – https://www.towardshealthcare.com/schedule-meeting
You can place an order or ask any questions, please feel free to contact us at sales@towardshealthcare.com
Powering Healthcare Leaders with Real-Time Insights: https://www.towardshealthcare.com/healthcare-intelligence-platform
Europe Region – +44 778 256 0738
North America Region – +1 8044 4193 44
APAC Region: +91 9356 9282 04
Web: https://www.towardshealthcare.com
Find us on social platforms: LinkedIn | Twitter | Instagram | Medium | Pinterest