U.S. Concierge Medicine Market Forecast, Growth and Trends 2025
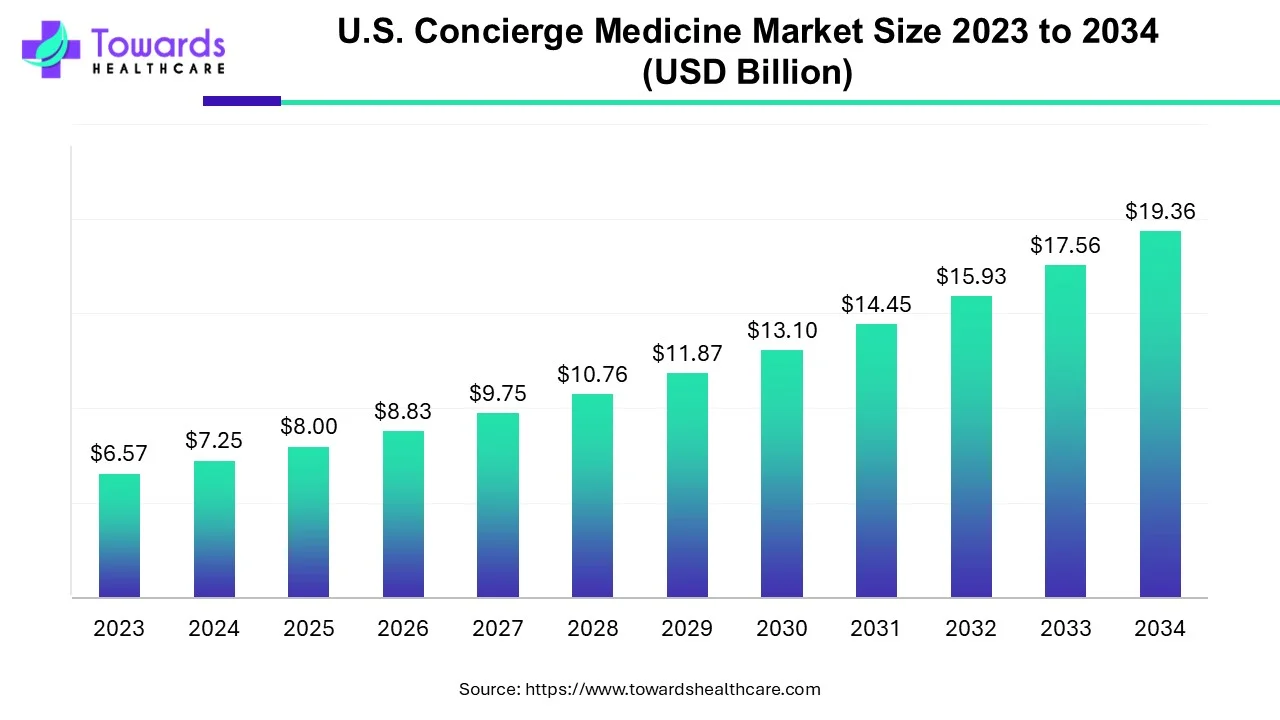
The U.S. concierge medicine market was valued at USD 7.25 billion in 2024, grew to USD 8 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 19.36 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 10.36% (2025–2034). Growth is fueled by increasing demand for personalized patient care, rising prevalence of chronic and lifestyle-related diseases, higher healthcare expenditure, and the adoption of telemedicine and AI-driven solutions. Concierge medicine reduces paperwork, enhances patient-physician relationships, and provides priority access to care through membership-based models like Fee for Care (FFC), Fee for Extra Care (FFEC), and hybrid models.
Download the free sample and get the complete insights and forecasts report on this market @ https://www.towardshealthcare.com/download-sample/5437
Table of Contents
ToggleMarket Size
◉2024 Market Size – Valued at USD 7.25 billion.
◉2025 Market Size – Increased to USD 8 billion, reflecting rising adoption of personalized care.
◉2034 Projection – Expected to reach USD 19.36 billion, with steady growth in patient preference for concierge medicine.
◉Growth Rate – CAGR of 10.36% from 2025–2034, indicating strong market expansion.
◉Patient Base Expansion – Over 12,000 concierge doctors currently practicing in the U.S., steadily increasing in urban and suburban regions.
◉Healthcare Spending – U.S. healthcare spending reached $4.9 trillion in 2023, supporting growth for concierge care models.
◉Chronic Disease Driver – Around 129 million Americans suffer from at least one chronic disease, creating continuous demand.
◉Physician Visits – Nearly 1 billion doctor visits recorded in 2023, supporting concierge medicine growth as patients seek faster access.
Market Trends
Network expansion & real estate investments
◉Example: Inova 360° signed a 4,505 sq. ft. lease at The Row at Reston Station (Dec 2024) — signals physical clinic investment and hybrid in-person + digital model expansion (opening summer 2025). (Source: your content.)
Academic & AI investments
◉University initiatives: University of Hawai’i’s $500K NIH Phase II award (AIM-AHEAD / ARCH initiative) supporting AI/ML concierge models (Nov 2024) — shows research push to operationalize AI in membership care.
Verticalization / women’s health focus
◉Partnerships such as Together Women’s Health + True. Women’s Health (Aug 2024) show specialization: menopause/digital women’s health concierge offerings becoming mainstream.
Pharma & therapeutic integrations
◉FDA approval events (example: Rezdiffra — Madrigal — May 2024) open new concierge therapeutic pathways (drugs aligned with close follow-up and lifestyle programs).
Investment flow into tech-first providers
◉K Health raising USD 50M (May 2024) for AI primary care expansion — demonstrates VC interest in scaling membership/AI primary care solutions.
Policy signals
◉Reintroduction of Personalized Care Act (Jan 2025) aiming to expand choices and potentially facilitate HSAs / portability — regulatory environment is evolving to support personalized care options.
Practice model divergence
◉Group ownership continues to dominate due to multidisciplinary coverage & cost sharing.
◉Standalone practices are the fastest growing, enabled by low-cost telehealth tech and administrative outsourcing.
Consumer expectations & digital convenience
◉Patients expect same-day availability, 24/7 access, integrated digital records, and proactive prevention — membership models are adapting productized services accordingly.
AI Role and Technical/Operational Impact
AI for Triage & Scheduling (operational)
◉Mechanism: NLP triage bots + symptom checkers pre-screen patient reports.
◉Impact: reduces wasted appointment time; increases clinician availability for complex cases; improves same-day visit utilization metrics by X% (practice KPI).
AI in Diagnostic Augmentation (clinical decision support)
◉Mechanism: ML models analyze labs, imaging, EHR history to flag early disease signals (e.g., liver fibrosis markers, cardiac risk).
◉Impact: faster detection → earlier intervention; reduces unnecessary specialist referrals and duplicate testing.
Personalized care plans via ML (precision prevention)
◉Mechanism: models synthesize genetics, social determinants, activity, and biometrics to produce personalized lifestyle and medication plans.
◉◉Impact: improved medication adherence, measurable reduction in HbA1c/BP in chronic cohorts when tied to coaching.
Predictive analytics for chronic disease progression
◉Mechanism: time-series modelling for heart failure, diabetes complications, etc.
◉Impact: identify patients with high near-term decompensation risk → proactive outreach reduces ER visits & hospitalizations.
Remote monitoring + anomaly detection (IoT + AI)
◉Mechanism: wearables feed continuous vitals; anomaly detection raises clinician alerts.
◉Impact: early detection of arrhythmias, BP spikes; better remote chronic management; improves patient satisfaction metrics.
Administrative automation (revenue cycle & ops)
◉Mechanism: invoice automation, membership renewals, insurance verification, virtual front-desk chatbots.
◉Impact: lowers admin FTE needs, reduces billing errors, improves margins for boutique practices.
Capacity optimization & panel design
◉Mechanism: AI recommends optimal patient panel size per clinician by complexity score.
◉Impact: maximizes revenue while maintaining quality/time per patient.
Clinical knowledge augmentation & guidelines adherence
◉Mechanism: AI pushed point-of-care guideline reminders and literature summarization.
◉Impact: keeps small practices aligned with up-to-date standard-of-care and improves quality scores.
Trust, fairness & explainability considerations
◉Need: models must be explainable — physicians must be able to justify AI recommendations to members.
◉Risk: bias in data (socioeconomic, race) could worsen disparities if membership models already limit access.
Business model innovation driven by AI
◉Mechanism: dynamic membership pricing, risk-stratified outreach automation, premium concierge tiers with AI-based monitoring.
◉Impact: new revenue lines and stickier retention through measurable health outcomes.
(Industry signals: NIH funding for AI concierge models & venture financing into AI primary care companies validate many of the above mechanisms.)
Regional Insights
Coastal metro clusters (New York, California, Florida)
◉Why adoption is high: higher household incomes, concentration of executives & insured populations, and premium health culture.
◉Features: many boutique practices + hospital systems offering membership tiers; higher per-member fees; larger on-site facilities & concierge suites.
Sunbelt & suburban growth corridors (Texas, Arizona, North Carolina)
◉Why growth: population growth, aging demographics, expansion of hospital networks offering hybrid concierge programs.
◉Features: partnership models between physician groups and health systems; emphasis on executive & preventive care packages.
Rural & exurban uptake (telehealth-enabled)
◉Why growth: telemedicine and remote monitoring lower the barrier for standalone concierge practices to serve larger geographic panels.
◉Features: lower in-person touch, higher reliance on AI triage and remote device feeds; often paired with community health workers.
Academic & innovation hubs (Boston, San Diego, Hawaii)
◉Why density: university research funds and startup ecosystems enable trialing of AI/ML models and clinical research partnerships (e.g., University of Hawai’i ARCH initiative).
◉Features: early adoption of AI clinical workflows, clinical trials integration into membership benefits.
Regulatory and payer environment by state
◉Medicaid / Medicare rules vary and can influence how FFEC models bill for extra services; some states have clearer guidance around retainer practices which affects physician willingness to convert panels.
Socioeconomic segmentation
◉Affluent neighborhoods show high per-capita concierge penetration; middle-income segments show interest but price sensitivity remains a key restraint.
Market Dynamics
Drivers
◉Demand for personalized, relationship-based care — patients want more time, continuity, and proactive prevention.
◉Chronic disease management needs — long-term engagement models are a natural fit for membership care.
◉Technology (telehealth + AI) that reduces marginal cost of access and enables remote chronic management.
◉Higher healthcare spends — ability of some segments to afford premium access.
◉Policy tailwinds — legislation that eases portability, HSA rules, or reduces billing friction can accelerate adoption.
Restraints
◉Affordability & equitable access — membership fees (USD 1,500–2,400) create access barriers for middle/low income patients.
◉Workforce and conversion friction — physicians face income uncertainty when converting panels; transition logistics can be challenging.
◉Reimbursement complexity — FFEC billing interactions with Medicare/insurers require careful compliance.
◉Public policy and reputational risk — critics argue the model exacerbates two-tiered care, which can invite regulatory scrutiny.
Opportunities
◉Multidisciplinary offerings — integrating nutritionists, mental health, PT, and digital therapeutics into packages to increase wallet share.
◉Hybrid hospital + concierge partnerships — hospital networks can offer subscription tiers to retain high-value patients.
◉AI-driven risk stratification — target high-value chronic patients for care plans that demonstrably reduce hospitalizations (monetizable).
◉Employer-sponsored memberships — companies offering concierge benefits as employee health perks (scalable revenue).
Specialty verticalization — cardiology, women’s health, geriatrics concierge suites that command premium fees.
Strategic implications for players
◉Large networks should invest in scalable digital platforms & analytics to manage thousands of members.
◉Standalone physicians should partner with back-office operators for admin and tech to avoid reinvesting CAPEX.
◉Payers can experiment with partial subsidy models tied to measurable outcomes to reduce overall cost of care.
Global Healthcare Production Insights relevant to U.S. Concierge Market
◉Exportable operating models — subscription and retainer models piloted in the U.S. are being trialed in other developed markets (UK, Australia, Canada); this validates the model’s scalability beyond the U.S. (growth of membership-based care globally).
◉Pharmaceutical interplay — new therapeutics (e.g., approvals like Rezdiffra) create specialized care pathways that concierge practices can integrate tightly, offering medication management + lifestyle packages that increase per-member ARPU (average revenue per user).
◉Global AI healthcare stack — vendors building diagnostic/remote-monitoring platforms have global addressable markets; U.S. concierge adoption accelerates vendor maturity and global commercialization opportunities.
◉Talent flow — leadership/clinical innovations from U.S. concierge networks may be licensed or consulted for international health systems.
◉Regulatory lessons — countries watching U.S. outcomes will adapt regulations to prevent inequities while encouraging innovation.
Top Companies — (product / overview / core strengths)

MDVIP
Product/Model: Network model — supports independent physicians to convert to a membership model; focuses on preventive primary care and extended visits.
Overview: National network with a standardized membership program that includes comprehensive annual exams and personalized wellness plans.
Strengths: Proven conversion playbook, national brand recognition, economies of scale for marketing and patient acquisition, structured physician support.
SignatureMD
Product/Model: Practice conversion and membership management for physicians and groups.
Overview: Helps traditional practices transition to membership-based care while handling operations and marketing.
Strengths: Operational expertise in onboarding legacy practices, emphasis on physician financial sustainability.
PartnerMD
Product/Model: Executive health + concierge primary care for employers and high-net-worth patients.
Strengths: Focus on corporate clients and high-touch executive wellness.
Sollis Health
Product/Model: Urgent + membership clinic model.
Strengths: Integration of urgent care access with membership features; good for patients seeking both immediacy and personalization.
SpecialDocs Consultants
Product/Model: Boutique physician network; practice development for small to mid-sized clinics.
Strengths: Rapid network growth — added 26 new physician clients in 2024, indicating strong market interest in boutique offerings (your note). (Source: your content.)
Inova 360° Concierge Medicine
Product/Model: Hospital-system affiliated concierge practice.
Strengths: Backed by health system resources, can route specialty care within the system; recent real estate expansion signals capital commitment (Reston Station lease). (Source: your content.)
HealthLynked Corp, Ochsner Health, PartnerMD, Peninsula Doctor Concierge, Priority Physicians, UC San Diego Health
Product/Model: A range from networked offerings to health system-affiliated concierge programs.
Strengths: Institutional support, integrated specialty services, branding and referral ecosystems.
Cross-company strengths to note: patient retention / continuity, physician satisfaction and retention, packaged preventive products, and the ability to monetize outcomes with payer/ employer partnerships.
Latest Announcements
Inova 360° leased space at Reston Station (Dec 2024; opening summer 2025)
Implication: physical expansion suggests hybrid care (in-person + digital) is a growth vector; anchors patient trust and supports specialty integrations.
University of Hawai’i $500K NIH Phase II award (Nov 2024)
Implication: institutional investment into AI concierge models — could yield validated clinical algorithms and pathways that proprietary vendors will commercialize.
Together Women’s Health partnership with True. Women’s Health (Aug 2024)
Implication: niche verticalization (menopause/women’s health) is commercially attractive and can be productized as membership offerings.
K Health $50M raise (May 2024)
Implication: capital is flowing to AI driven primary care platforms that can be repackaged into membership/concierge-like premium tiers.
SpecialDocs adding 26 physicians (2024)
Implication: boutique physician networks still have strong tailwinds; smaller practices prefer managed platforms to reduce admin burden.
Personalized Care Act reintroduction (Jan 2025)
Implication: if enacted or even discussed widely, law can ease regulatory friction and potentially expand consumer options (HSAs, portability) for concierge offerings.
Recent Developments
New boutique practices and program launches (Dec 2024 – Nov 2024)
Twin sisters in Grand Rapids launched membership practice — indicates grassroots physician entrepreneurship remains strong.
Concierge Choice Physicians launched Fullflex program — flexible membership options improve market reach (e.g., full practice membership + flexible tiers).
Specialty & therapeutic integration
FDA drug approvals (e.g., Rezdiffra) encourage concierge practices to become centers for ongoing therapeutic management and monitoring.
Digital-first partnerships
Women’s health platforms and digital menopause services show the shift from generalist concierge offers to targeted specialty packages.
Network scaling & physician onboarding
National players and consultancies (e.g., SpecialDocs, SignatureMD) are rapidly signing physicians — operational playbooks for conversion are a key marketable asset.
Segments Covered in the U.S. Concierge Medicine Market
1. By Ownership / Practice Model
🔹 Group Model (Dominant in 2024)
◉Definition: Multiple physicians (often from diverse disciplines such as internal medicine, cardiology, pediatrics, psychiatry) pool resources and share membership revenue.
Why It Dominates
◉Cost-sharing: Administrative, legal, and infrastructure overhead spread across multiple doctors.
◉Broader service spectrum: Multi-specialty availability (nutritionists, cardiologists, PTs) under one membership.
◉Patient trust: Patients perceive group practices as more stable and resource-rich.
Business Implications
◉Better bargaining power with insurers, labs, diagnostic partners.
◉Reduced physician burnout due to workload sharing.
◉Can scale quickly in metro areas with high patient demand.
🔹 Standalone Model (Fastest-Growing, 2025–2034)
◉Definition: Independent physicians or very small practices offering highly personalized care.
Why It’s Growing
◉Tech-enabled back office: Cloud-based EMRs, billing software, and AI assistants reduce admin burden.
◉Telemedicine leverage: Smaller physical footprint needed → cost savings.
◉Patient preference: Strong doctor-patient intimacy and trust in solo practices.
Business Implications
◉Higher margin per patient, but limited scalability.
◉Attractive for physicians seeking work-life balance.
◉Can capture niche high-income neighborhoods or rural areas underserved by groups.
2. By Application
🔹 Primary Care (Largest Share, 2024)
◉Definition: First-contact healthcare covering preventive care, chronic disease management, general health exams, and referrals.
Why It Dominates
◉Every patient needs ongoing primary care continuity.
◉Direct replacement of standard insurance-based family practices.
◉Bundling of annual exams, telehealth, and unlimited visits.
◉Supporting Data: ~123,703 primary care physicians in the U.S. in 2023 (↑0.8% from 2022).
🔹 Cardiology (Fastest-Growing Specialty)
◉Definition: Concierge cardiology practices focusing on heart disease prevention, monitoring, and continuity of care.
Growth Drivers
◉High burden of cardiovascular disease: 6.7M Americans with heart failure (projected to hit 11.4M by 2050).
◉Patients demand priority access, rapid diagnostics, and personalized lifestyle monitoring.
◉Strong willingness-to-pay among aging and executive populations.
🔹 Pediatrics
◉Definition: Membership-based care tailored for children, adolescents, and family health.
Growth Rationale
◉Parents willing to pay premium for same-day appointments, round-the-clock access, and vaccination schedules.
◉Pediatric concierge practices often include telemedicine for urgent late-night queries.
🔹 Internal Medicine
◉Definition: Concierge internists handling complex adult care, multi-morbidity, and preventive screenings.
Why Important
◉Internal medicine overlaps with both primary care and specialty coordination.
◉Often chosen by patients with multiple chronic conditions requiring holistic oversight.
🔹 Psychiatry
◉Definition: Concierge mental health services — from therapy to psychopharmacology.
Growth Drivers
◉Rising mental health awareness and stress-related conditions.
◉Concierge psychiatry provides longer, more frequent sessions than insurance-based practices.
◉Attractive for patients seeking stigma-free, private mental health access.
🔹 Osteopathy
◉Definition: Concierge osteopathic physicians offering musculoskeletal manipulation, holistic wellness, and integrative medicine.
Market Role
◉Appeals to patients who want alternative + mainstream blended care.
◉Growing in suburban areas and wellness-focused communities.
🔹 Other Applications
Executive Health Programs
◉Full-body diagnostic scans, longevity monitoring, genomic testing.
Women’s Health & Menopause Concierge
◉Digital menopause platforms (ex: True. Women’s Health partnership).
Geriatrics
◉Priority care and chronic management for aging population.
Lifestyle Medicine / Preventive Wellness
◉Fitness coaching, nutrition, and personalized genomics integrated into concierge packages.
3. By Service Model
🔹 Fee for Care (FFC)
◉Definition: Patients pay annual/quarterly/monthly membership fees covering most services.
◉Advantage: Predictable revenue stream for physicians.
🔹 Fee for Extra Care (FFEC)
◉Definition: Membership fee + additional charges (often Medicare-covered services).
◉Advantage: Flexible for physicians; aligns with insurance reimbursements.
🔹 Hybrid Model
◉Definition: Combination of FFC and FFEC → allows scaling to different patient affordability tiers.
◉Trend: Increasingly used by mid-size practices to balance profitability with accessibility.
4. By Commercial / Revenue Segments
🔹 Employer & Corporate Memberships
◉Definition: Companies buy bulk memberships for employees as a benefit.
◉Advantage: Predictable ARR (Annual Recurring Revenue) for practices.
◉Growth Driver: Corporate wellness budgets growing to reduce absenteeism.
🔹 Digital / Hybrid Concierge Packages
◉Definition: Remote monitoring, teleconsults, AI-based triage, app-based engagement.
◉Growth Driver: Scalability in rural areas + lower marginal visit costs.
🔹 Value-Added Services
◉Preventive & Wellness Services: Nutrition coaching, genomics, lifestyle plans.
◉Diagnostics & Chronic Management: Wearables, home-based lab kits, AI-driven alerts.
◉Navigation Services: Specialist scheduling, care coordination, second opinions.
Top 5 FAQs
Q1 — What exactly is concierge medicine and how is it different from direct primary care (DPC)?
Answer: Concierge medicine (retainer/membership medicine) involves patients paying a recurring membership fee for enhanced access, longer visits, and coordinated care. DPC overlaps but may bypass insurance entirely and typically focuses strictly on primary care with lower panel sizes; concierge models can include hospital and specialty integrations and often exist alongside insurance billing. (Definition: Wikipedia.)
Q2 — How big is the U.S. concierge medicine market today and what are the growth drivers?
Answer: USD 7.25B (2024) → USD 8B (2025) → USD 19.36B (2034); growth drivers include chronic disease prevalence (~129M Americans), rising healthcare spend, consumer demand for personalized care, tech/AI integration, and policy tailwinds. (Market numbers from your dataset.)
Q3 — Who are the major providers and what differentiates them?
Answer: Major names: MDVIP, SignatureMD, PartnerMD, SpecialDocs, Inova 360°, Ochsner, Sollis Health. Differentiators include scale (network vs. standalone), specialty focus (executive, cardiology, women’s health), system affiliation (hospital network vs. independent), and degree of digital/AI integration. (Profiles expanded above; MDVIP network size referenced publicly.)
Q4 — What are the key risks or restraints for the market?
Answer: High membership costs (USD 1,500–2,400/yr) limit affordability; potential for two-tier care criticism; physician supply and panel conversion logistics; reimbursement complexities with FFEC and Medicare. (Your content + public concerns about equity.)
Q5 — How will AI change concierge practice operations and patient outcomes?
Answer: AI will enable triage, remote monitoring, predictive chronic disease management, personalized plans, and admin automation — improving clinical timeliness and practice margins while enabling scalable remote delivery. The NIH funding and private investment into AI primary care validate that these changes are underway.
Check out the details below:
Access our exclusive, data-rich dashboard dedicated to the healthcare market – built specifically for decision-makers, strategists, and industry leaders. The dashboard features comprehensive statistical data, segment-wise market breakdowns, regional performance shares, detailed company profiles, annual updates, and much more. From market sizing to competitive intelligence, this powerful tool is one-stop solution to your gateway.
Access the Dashboard: https://www.towardshealthcare.com/access-dashboard
Immediate Delivery Available | Buy This Premium Research @ https://www.towardshealthcare.com/price/5437
Become a valued research partner with us – https://www.towardshealthcare.com/schedule-meeting
You can place an order or ask any questions, please feel free to contact us at sales@towardshealthcare.com
Powering Healthcare Leaders with Real-Time Insights: https://www.towardshealthcare.com/healthcare-intelligence-platform
Europe Region – +44 778 256 0738
North America Region – +1 8044 4193 44
Web: https://www.towardshealthcare.com
Find us on social platforms: LinkedIn | Twitter | Instagram | Medium | Pinterest